About VPN
What is VPN
Virtual private network (VPN) is used to set up a secure encrypted communication channel between two communicating peers. You can use a VPN service to enable communication between a local traditional data center and a classic network or VPC created on the system. The system supports only IPsec VPN.
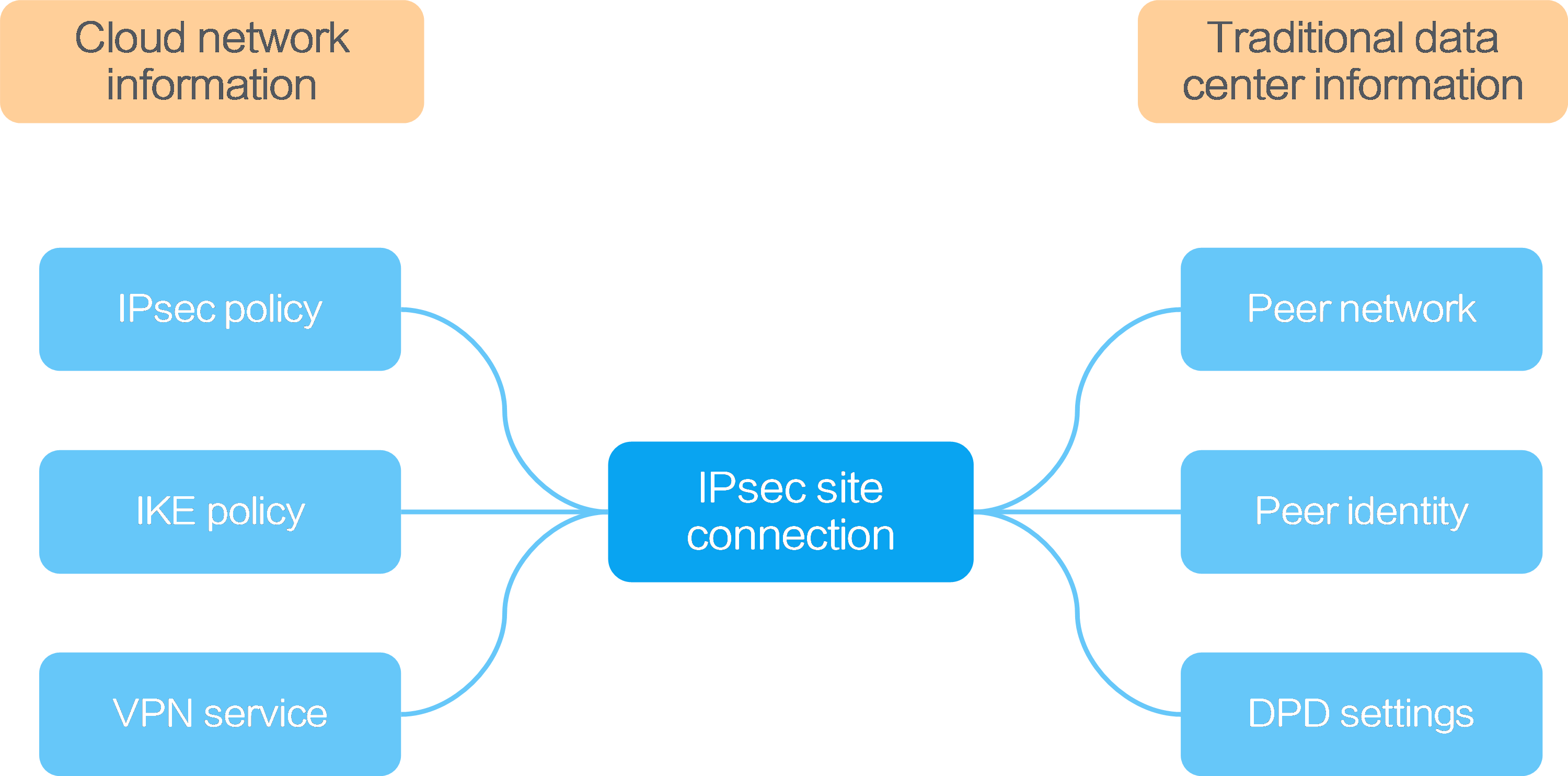
The VPN feature of the system contains the IPsec policy, IKE policy, VPN service, and IPsec site connection functions. An IPsec site connection connects a cloud network to a traditional data center based on information of the cloud network and the traditional data center. The cloud network information includes the IPsec policy, IKE policy, and VPN service. The traditional data center information includes the peer network, peer identify, and DPD settings.
Figure-1 Functions of VPN
IPsec policy—IPsec is a Layer 3 VPN technology that transmits data in a secure channel established between two endpoints to offer high-quality, cryptography-based security for IP communications. Such a secure channel is usually called an IPsec tunnel. An IPsec policy specifies the security protocol, encryption method, and authentication algorithm that are used for data transmission.
IKE policy—IKE negotiates SAs for IPsec and transfers the SAs to IPsec, and IPsec uses the SAs to protect IP packets. An IKE policy specifies the encryption and authentication algorithm used for IPsec tunnel negotiation.
VPN service—A VPN service specifies the cloud network resource that requires a VPN connection.
IPsec site connection—A IPsec site connection specifies the settings for connecting a local network to a peer, including the IPsec policy, IKE policy, VPN service, peer network, peer identify, and DPD settings.
Application scenarios
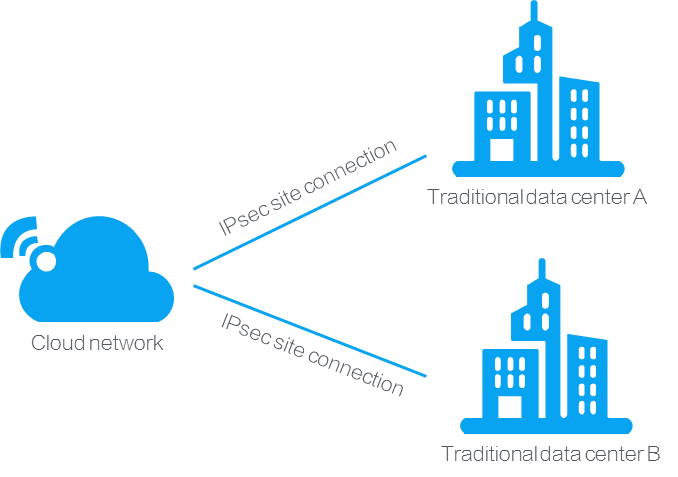
Single-site VPN connection—Connects a cloud network to a local traditional data center in a VPN service, as shown in Figure-2.
Figure-2 Single-site VPN connection
Multi-site VPN connection—Connects a cloud network to multiple traditional data centers in a VPN service, as shown in Figure-3. The subnets of the traditional data centers cannot overlap.
Figure-3 Multi-site VPN connection
Restrictions and guidelines
You can bind a cloud network to one VPN service.
You must configure security groups to enable communication among the local and remote VMs in the same VPN.
Relationship with other services
Table-1 Relationship with other services
|
Service |
Relationship |
|
Classic network/VPC |
Network resources interconnected through VPN. Classic networks and VPCs are different virtual networks provided by the system. For more information about classic networks and VPCs, see the content of classic networks and VPC networks. |
Concepts
This section lists common terms used in IPsec and IKE. You can skip this section if you have basic knowledge of IPsec and IKE.
IPsec
IPsec is a security framework that has the following protocols and algorithms:
Authentication Header (AH).
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP).
Internet Key Exchange (IKE).
Algorithms for authentication and encryption.
IPsec security protocols
IPsec has two security protocols, AH and ESP. AH provides authentication, and ESP provides both authentication and encryption. You can use AH or ESP alone or use them together to improve security.
IPsec encapsulation modes
IPsec supports the following encapsulation modes:
Transport mode—The security protocols protect the upper layer data of an IP packet. The transport mode is typically used for protecting host-to-host communications.
Tunnel mode—The security protocols protect the entire IP packet. The tunnel mode is typically used for protecting gateway-to-gateway communications.
The VPN service supports only the tunnel mode.
Security association
A security association (SA) is an agreement negotiated between two communicating parties called IPsec peers. An SA includes the following parameters for data protection:
Security protocols (AH, ESP, or both).
Encapsulation mode (transport mode or tunnel mode).
Authentication algorithm (HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA1).
Encryption algorithm (DES, 3DES, or AES).
Shared keys and their lifetimes.
An SA can be set up manually or through IKE. The VPN service supports only the IKE negotiation mode.
IKE
About IKE
IKE negotiates SAs for IPsec and transfers the SAs to IPsec, and IPsec uses the SAs to protect IP packets.
IKE allows two peers to establish an IKE SA and use it to establish IPsec SAs.
The shared keys are calculated by using the DH algorithm. With this algorithm, two peers can exchange keying material and then use the material to calculate unique shared keys for each IPsec SA.
IKE negotiation process
IKE negotiates keys and SAs for IPsec in two phases:
Phase 1—The two peers establish an IKE SA, a secure, authenticated channel for communication.
Phase 2—Using the IKE SA established in phase 1, the two peers negotiate to establish IPsec SAs.
Phase 1 negotiation can use either main mode or aggressive mode. The VPN service supports only main mode.
IKE security mechanism
IKE has a series of self-protection mechanisms and supports secure identity authentication, key distribution, and IPsec SA establishment on insecure networks.
Identity authentication
The IKE identity authentication mechanism is used to authenticate the identity of the communicating peers. IKE provides pre-shared key authentication, RSA signature authentication, and DSA signature authentication. The VPN service supports only pre-shared key authentication which allows two communicating peers to use the pre-configured shared key for identity authentication.
DH algorithm
The DH algorithm is a public key algorithm. With this algorithm, two peers can exchange keying material and then use the material to calculate the shared keys. Due to the decryption complexity, a third party cannot decrypt the keys even after intercepting all keying materials.
PFS
The Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) feature is a security feature based on the DH algorithm. After PFS is enabled, an additional DH exchange is performed in IKE phase 2 to make sure IPsec keys have no derivative relations with IKE keys and a broken key brings no threats to other keys.