Configuring shared network ports
About shared network ports
Typically, a server has dedicated network port and shared network port settings in the BMC/HDM configuration in BIOS.
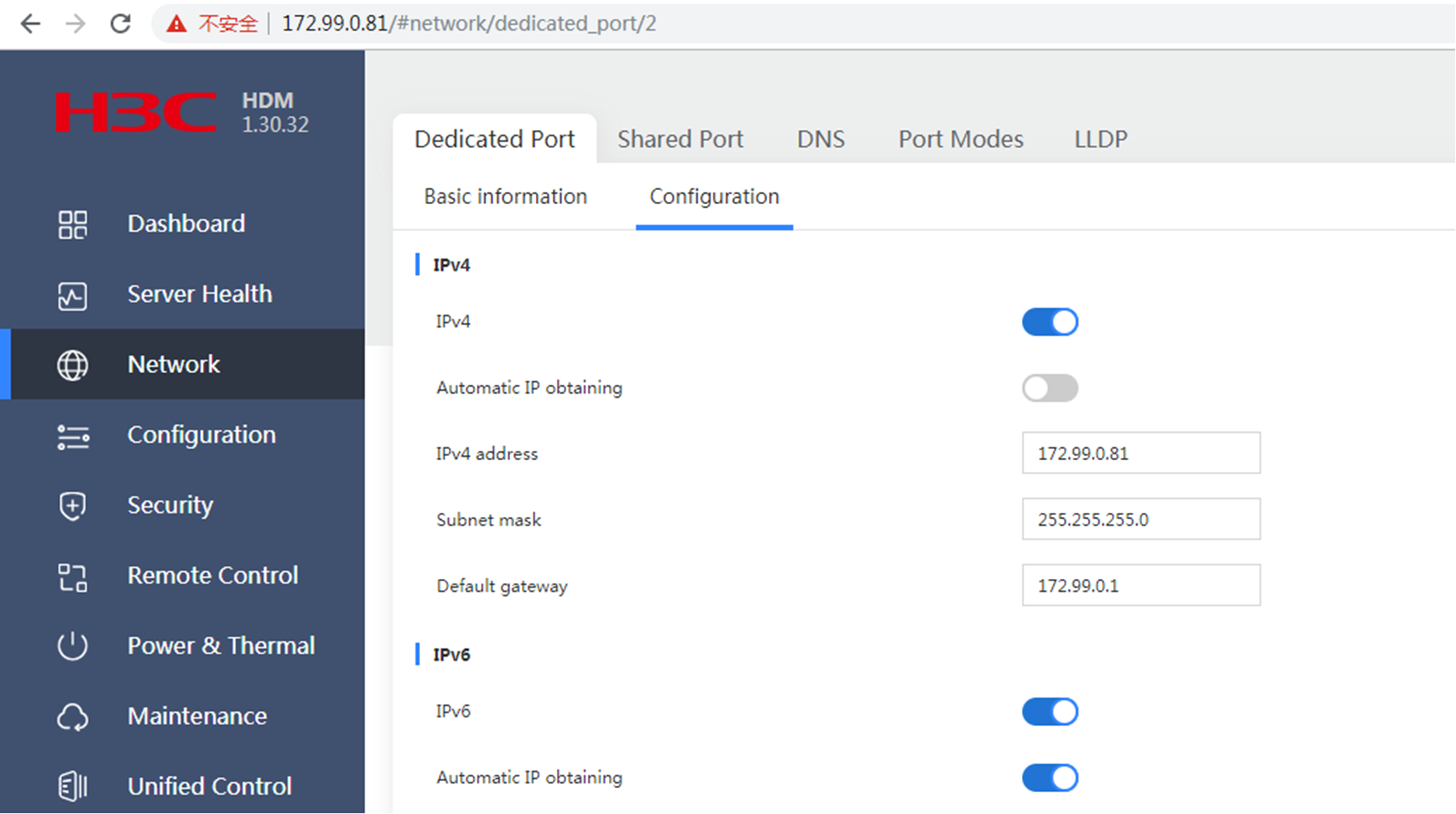
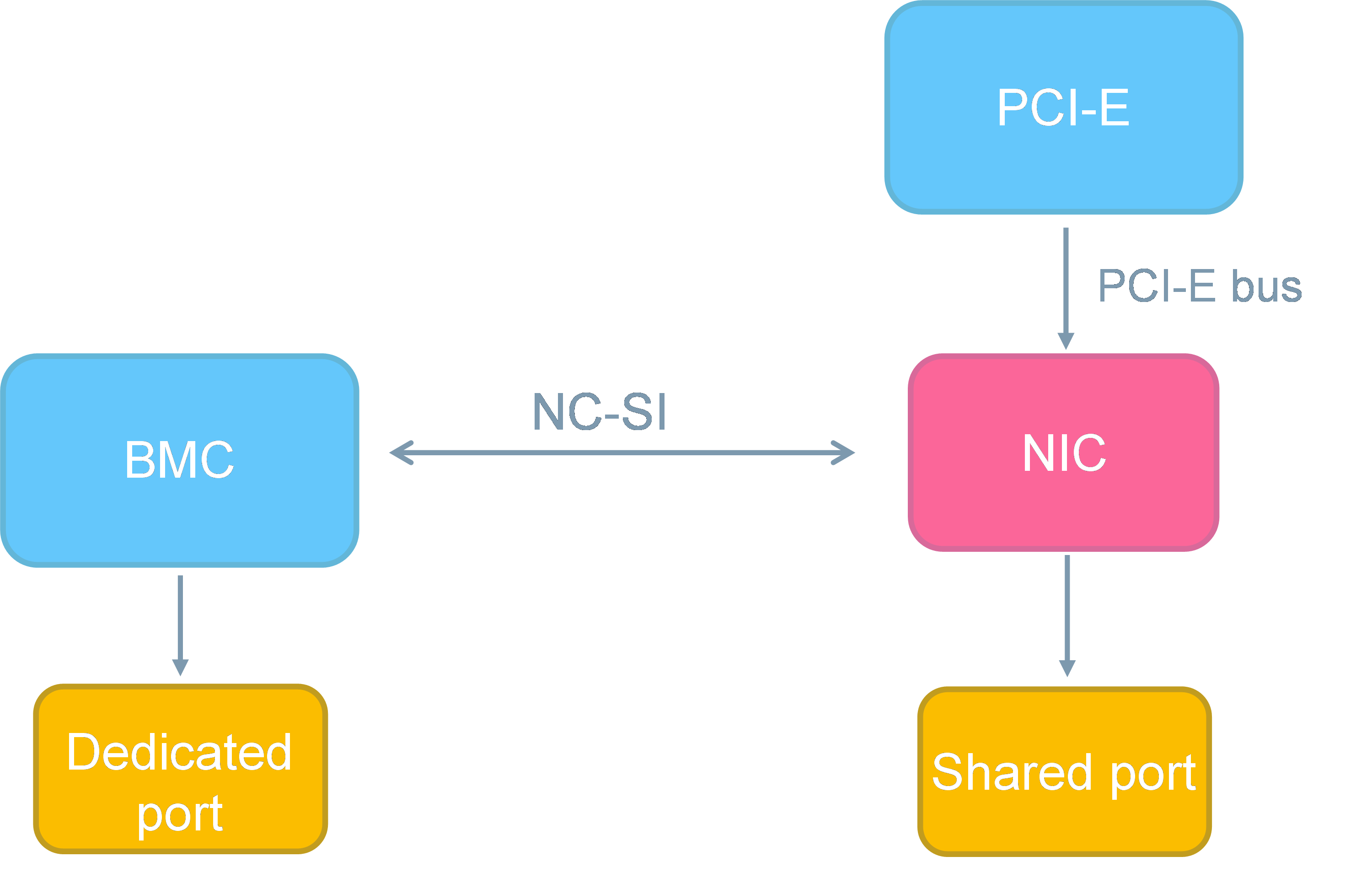
Dedicated and shared network ports are embedded on the mainboard of the server. A dedicated network port is the management port of BMC/HDM. You can access the management interface of BMC/HDM by entering the IP address configured on the dedicated network port in the browser. After configuring the shared network interface and connecting a network cable, you can also access the BMC/HDM management interface by entering the IP address configured on the shared network port. You can configure the ports in BIOS or through a browser.
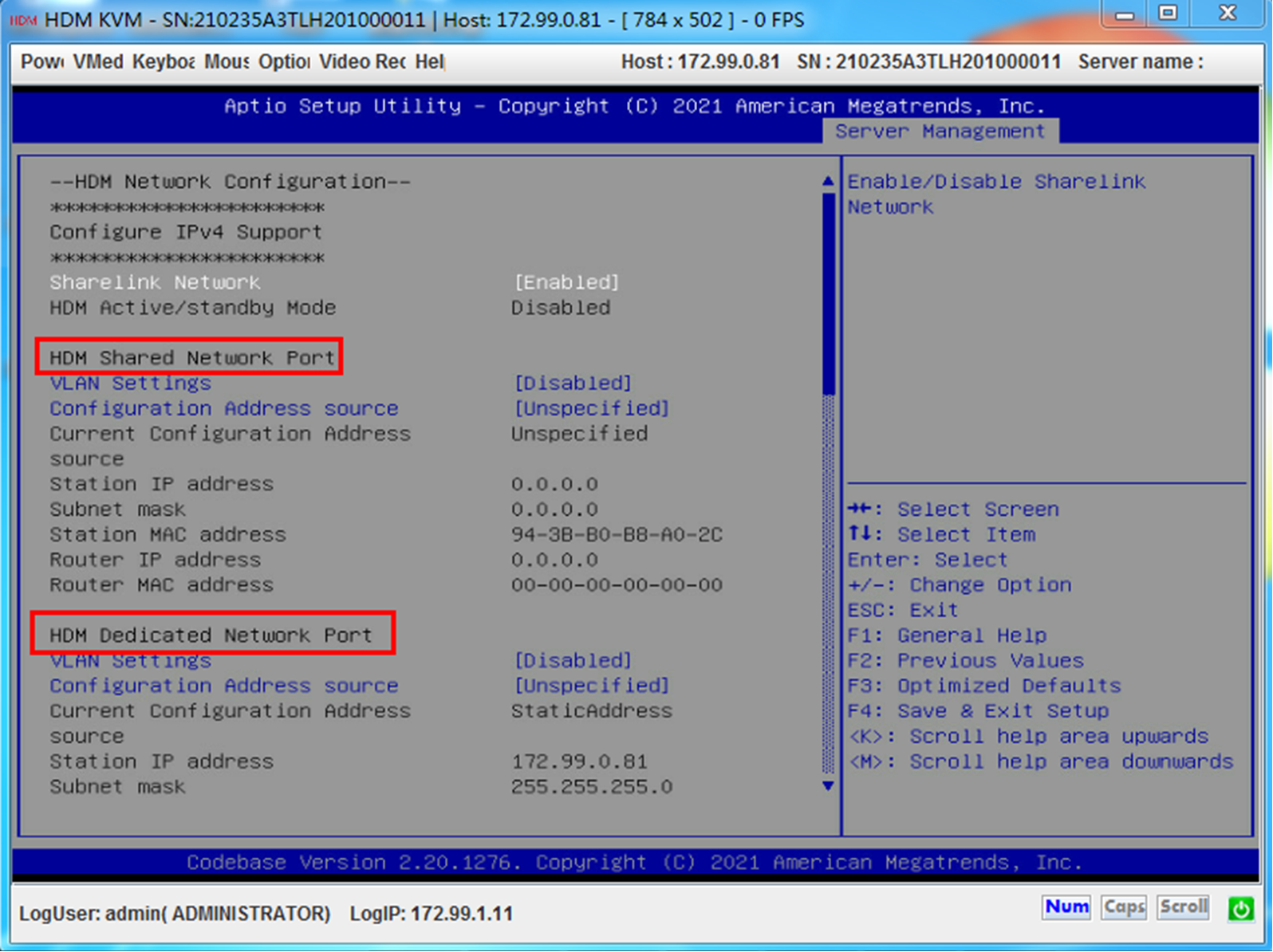
The following uses a 4900 G3 server as an example. The following figure shows the configuration of the two ports in BIOS.
Configure the dedicated network port:
Ports on the 4900 G3 server:
Mechanism
A shared network port is implemented based on network controller sideband interface (NC-SI) technology, which provides a connection between a baseboard management controller (BMC) and Ethernet controller. It enables a BMC chip to use the network interface on the motherboard like an independent management network interface.
Shared network port and bare metal service
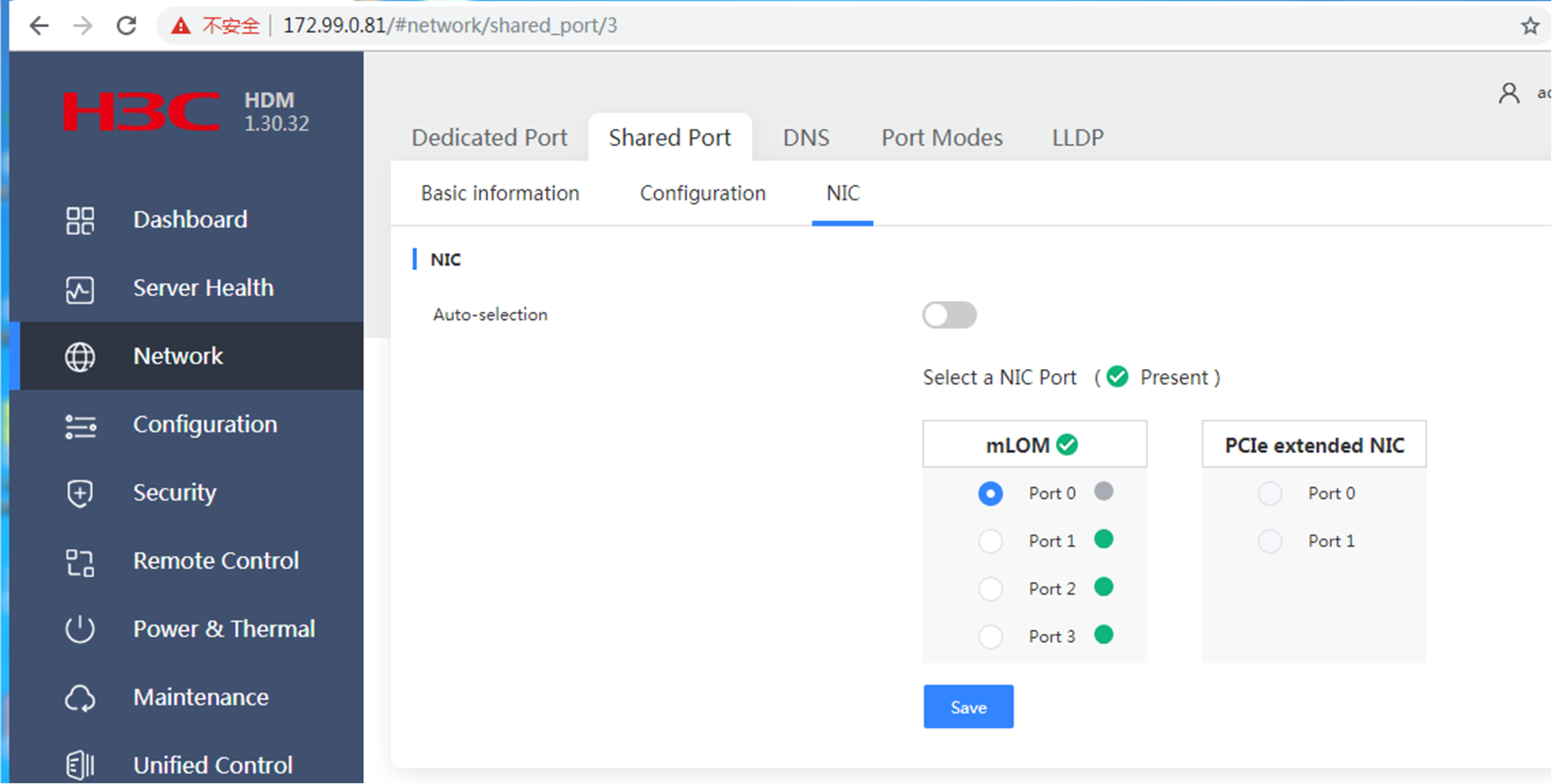
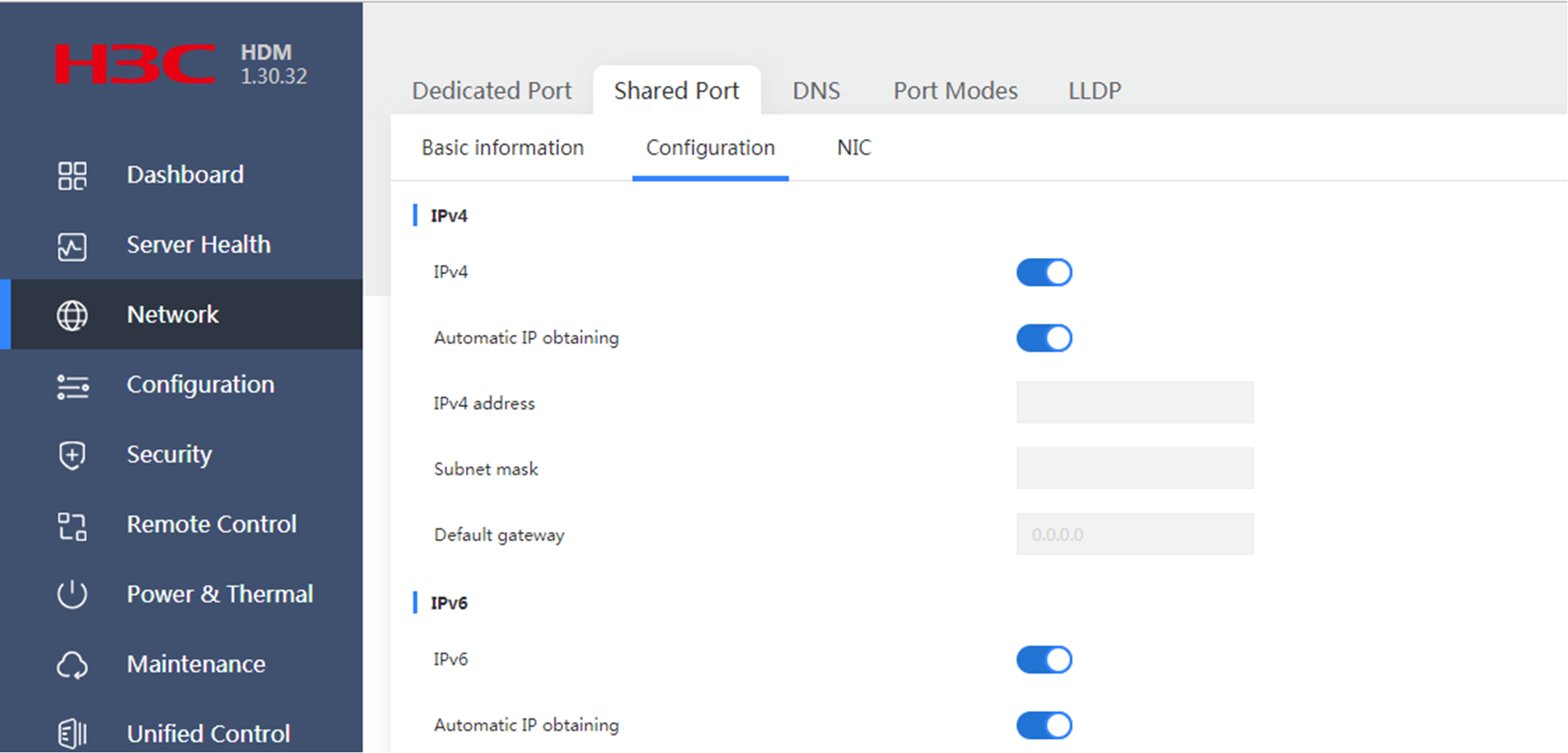
The shared network port is enabled with automatic IP obtaining and an mLOM network adapter (NIC) is selected when the server was shipped. When the server is connected to the bare metal service network, the server can obtain an IP address automatically from the address pool without power-on or joining any bare metal resource pool if the PXE network port is a shared network port. The IP address obtained through a PEX network port is automatically released after bare metal discovery. The IP address obtained through a shared network port will not be automatically released after bare metal discovery.
As shown in the figure, the default gateway at 172.99.1.53 is the NIC address for bare metal compute node discovery, and the automatically obtained IP address 172.99.1.230 belongs to the address pool with an IP range of 172.99.1.216,172.99.1.230,255.255.255.0.
The output on the bare metal compute node:
[root@ironnode50 ironic-inspector]# cat /var/lib/dnsmasq/dnsmasq.leases
1635770932 94:3b:b0:b8:a0:2c 172.99.1.230 HDM210235A3TLH201000011 01:94:3b:b0:b8:a0:2c
1635770817 60:0b:03:6f:4b:89 172.99.1.229 * 01:60:0b:03:6f:4b:89
1635770920 94:3b:b0:b8:a3:c8 172.99.1.227 HDM210235A3TLH201000020 01:94:3b:b0:b8:a3:c8
1635770808 60:0b:03:6f:46:cd 172.99.1.226 * 01:60:0b:03:6f:46:cd
1635769550 94:3b:b0:b8:a4:ee 172.99.1.223 HDM210235A3TLH201000017 01:94:3b:b0:b8:a4:ee
1635770267 0c:da:41:1d:c3:8a 172.99.1.222 ubuntu *
1635770887 0c:da:41:1d:e8:b2 172.99.1.224 * *
1635770875 0c:da:41:1d:c2:ad 172.99.1.225 * *
In a production environment, dozens or even hundreds of bare metal servers exist and the addresses in the DHCP address pools might be used up by a large number of shared network ports. This can cause failure to discover new bare metal servers by the system.
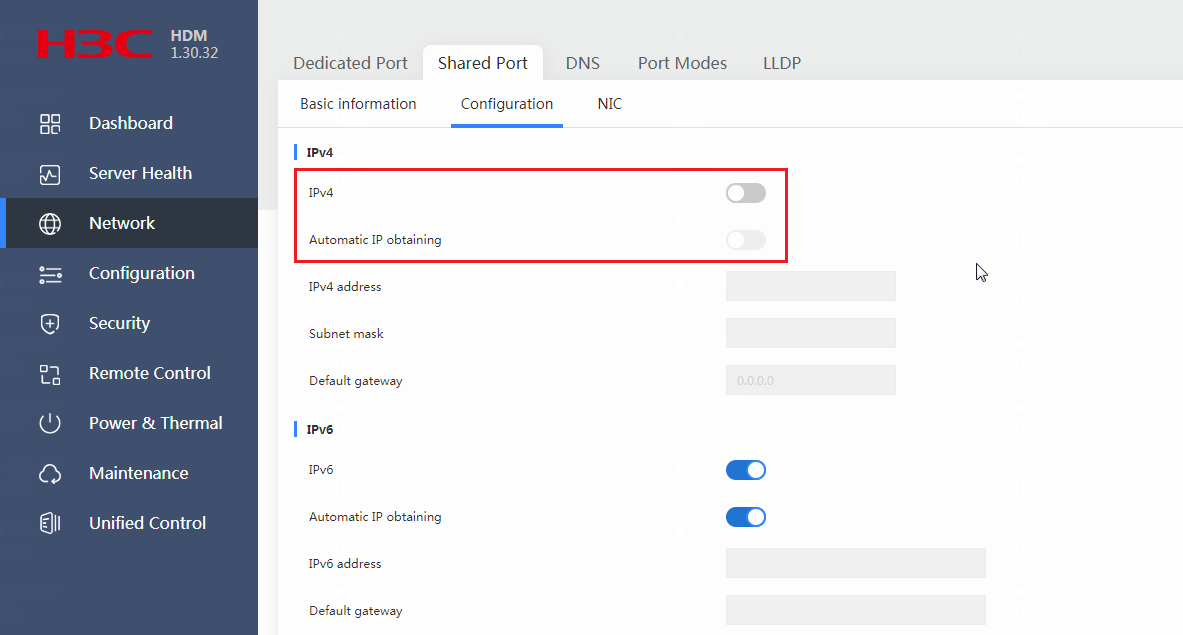
To avoid this issue, disable Automatic IP obtaining and IPv4 for the shared network port before you start discovering and deploying a bare metal server, and save the configuration.
You must disable both Automatic IP obtaining and IPv4 for the shared network port. If you disable only Automatic IP obtaining, the IP address that has been obtained cannot be reclaimed.