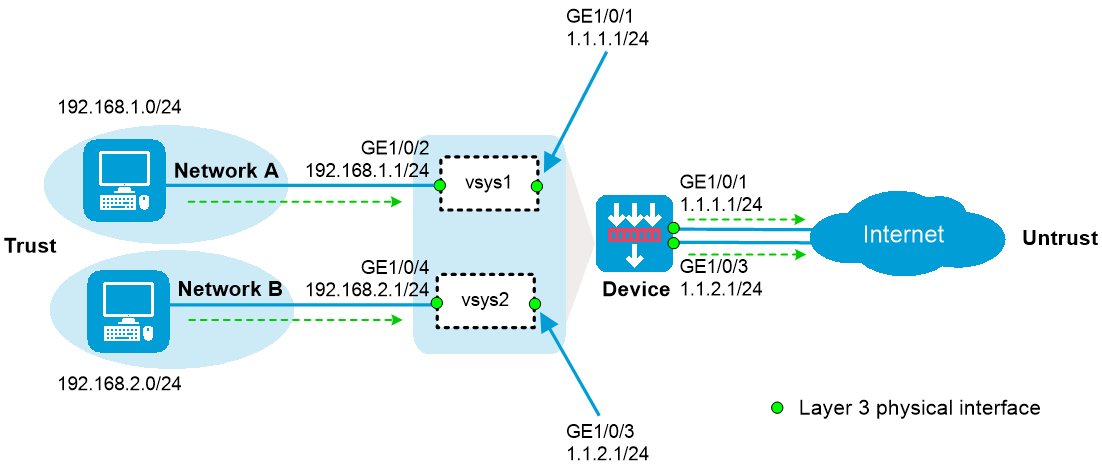
As shown in Figure 1:
The device acts as a security gateway.
The internal network is divided into Network A for the R&D department and Network B for non-R&D departments. Users in Network A and Network B are isolated.
In Network A, only users in subnet 192.168.1.128/25 can use independent public network interfaces to access the Internet. In Network B, all users can use independent public network interfaces to access the Internet.
This configuration example was created and verified on E8371 of the F5000-AI160 device.
1. Create vSystem vsys1 and assign interfaces to the vSystem:
# Create vSystem vsys1 and configure a description for the vSystem.
<Device> system-view
[Device] vsys vsys1
[Device-vsys-2-vsys1] description vsys-1
# Assign interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to vSystem vsys1.
[Device-vsys-2-vsys1] allocate interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
Some configurations on the interface are removed.
[Device-vsys-2-vsys1] allocate interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
Some configurations on the interface are removed.
[Device-vsys-2-vsys1] quit
2. Log in to vSystem vsys1, assign IP addresses to interfaces, and add interfaces to security zones:
# Log in to vSystem vsys1.
[Device] switchto vsys vsys1
<Device-vsys1> system-view
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
[Device-vsys1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 1.1.1.1 24
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[Device-vsys1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] ip address 192.168.1.1 24
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
# Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device-vsys1] security-zone name trust
[Device-vsys1-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
[Device-vsys1-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device-vsys1] security-zone name untrust
[Device-vsys1-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-vsys1-security-zone-Untrust] quit
3. Configure settings for routing. This example configures a static route. In the route, the next hop IP address is 1.1.1.2 for users in vSystem vsys1 to access the Internet.
[Device-vsys1] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 1.1.1.2
4. Configure a rule named trust-untrust in the IPv4 security policy to allow users in subnet 192.168.1.128/25 to access the Internet.
[Device-vsys1] security-policy ip
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.1.128 25
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] quit
[Device-vsys1-security-policy-ip] quit
5. Configure NAT:
# Configure ACL 2000, and create a rule to permit the packets only from 192.168.1.128/25 to be translated.
[Device-vsys1] acl basic 2000
[Device-vsys1-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.128 0.0.0.127
[Device-vsys1-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Enable outbound dynamic NAT with Easy IP on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 so that NAT translates the source addresses of the packets matching the ACL and destined for the Internet into the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
[Device-vsys1] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] nat outbound 2000
6. Return to the default vSystem from vSystem vsys1.
[Device-vsys1-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] return
<Device-vsys1> quit
[Device]
1. Create vSystem vsys2 and assign interfaces to the vSystem:
# Create vSystem vsys2 and configure a description for the vSystem.
[Device] vsys vsys2
[Device-vsys-3-vsys2] description vsys-2
# Assign interfaces GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/4 to vSystem vsys2.
[Device-vsys-3-vsys2] allocate interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
Some configurations on the interface are removed.
[Device-vsys-3-vsys2] allocate interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
Some configurations on the interface are removed.
[Device-vsys-3-vsys2] quit
2. Log in to vSystem vsys2, assign IP addresses to interfaces, and add interfaces to security zones:
# Log in to vSystem vsys2.
[Device] switchto vsys vsys2
<Device-vsys2> system-view
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces.
[Device-vsys2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] ip address 1.1.2.1 24
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] quit
[Device-vsys2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] ip address 192.168.2.1 24
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/4] quit
# Add interfaces to security zones.
[Device-vsys2] security-zone name trust
[Device-vsys2-security-zone-Trust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/4
[Device-vsys2-security-zone-Trust] quit
[Device-vsys2] security-zone name untrust
[Device-vsys2-security-zone-Untrust] import interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-vsys2-security-zone-Untrust] quit
3. Configure settings for routing. This example configures a static route. In the route, the next hop IP address is 1.1.2.2 for users in vSystem vsys2 to access the Internet.
[Device-vsys2] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 1.1.2.2
4. Configure a rule named trust-untrust in the IPv4 security policy to allow users in subnet 192.168.2.0/24 to access the Internet.
[Device-vsys2] security-policy ip
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip] rule name trust-untrust
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] source-zone trust
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] destination-zone untrust
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] source-ip-subnet 192.168.2.0 24
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] action pass
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip-1-trust-untrust] quit
[Device-vsys2-security-policy-ip] quit
5. Configure NAT:
# Configure ACL 2000, and create a rule to permit the packets only from 192.168.2.0/24 to be translated.
[Device-vsys2] acl basic 2000
[Device-vsys2-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
[Device-vsys2-acl-ipv4-basic-2000] quit
# Enable outbound dynamic NAT with Easy IP on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3 so that NAT translates the source addresses of the packets matching the ACL and destined for the Internet into the IP address of interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/3.
[Device-vsys2] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/3
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] nat outbound 2000
6. Return to the default vSystem from vSystem vsys2.
[Device-vsys2-GigabitEthernet1/0/3] return
<Device-vsys2> quit
[Device]
# Verify that the vSystems are running correctly on the device. The device has three active vSystems.
[Device] display vsys
ID Name Status Description
1 Admin Active Default
2 vsys1 Active vsys-1
3 vsys2 Active vsys-2
# Verify that users in subnet 192.168.1.128/25 can access the Internet.
C:\> ping 3.3.3.3
Pinging 3.3.3.3 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=51ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=44ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 3.3.3.3:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 51ms, Average = 24ms
# Verify that users in subnet 192.168.2.0/24 can access the Internet.
C:\> ping 3.3.3.3
Pinging 3.3.3.3 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=25ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=36ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Reply from 3.3.3.3: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255
Ping statistics for 3.3.3.3:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 36ms, Average = 16ms
#
vsys vsys1 id 2
description vsys1
allocate interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.1
#
vsys vsys2 id 3
description vsys2
allocate interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.2
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.1
vlan-type dot1q vid 10
#
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.2
vlan-type dot1q vid 20
#
ip route-static vpn-instance vsys1 10.20.0.0 24 vpn-instance vsys2
ip route-static vpn-instance vsys2 10.10.0.0 24 vpn-instance vsys1
#
switchto vsys vsys1
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.1
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface vSys-interface2
#
security-policy ip
rule 0 name vpc1
action pass
source-zone trust
destination-zone untrust
rule 1 name vpc2
action pass
source-zone untrust
destination-zone trust
#
switchto vsys vsys2
#
security-zone name Trust
import interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1.2
#
security-zone name Untrust
import interface vSys-interface3
#
security-policy ip
rule 0 name vpc1
action pass
source-zone trust
destination-zone untrust
rule 1 name vpc2