Configure storage replication-based disaster recovery
You can use storage replication-based disaster recovery regardless of whether storage arrays support storage replication adapters (SRAs) or not.
|
SRAs enable SRM to discover storage systems, replicate LUNs, and test and perform disaster recovery. When SRM tests disaster recovery, runs scheduled recovery, or runs failure recovery, SRAs offer resources to SRM and cooperate with SRM in disaster recovery automation in a virtualization environment. |
Application scenarios
Storage replication-based disaster recovery is applicable to data centers in homogeneous clouds where the same CAS CVM version is deployed on the protected and recovery sites and the protected objects are VMs. It can reduce RPO and RTO to minutes and copy data between storage arrays through synchronous or asynchronous replication.
Configuration environment
CAS edition—CAS Enterprise or Enhanced Enterprise Edition with DRM licensed, E0536 and later.
Storage—Use storage resources that meet the following requirements:
Storage automation support—MacroSAN, HPE 3PAR, HPE Primera (E0709 and later), ONEStor (E0709 and later), and Nimble storage (E0710P01 and later).
3PAR version—3.2.2.709 or later, with support for remote copy and active-active replication (licensed by using Peer Persistence License). The storage servers on the protected and recovery sites must use the same 3PAR version.
HPE storage array—With support for remote replication.
Mechanisms
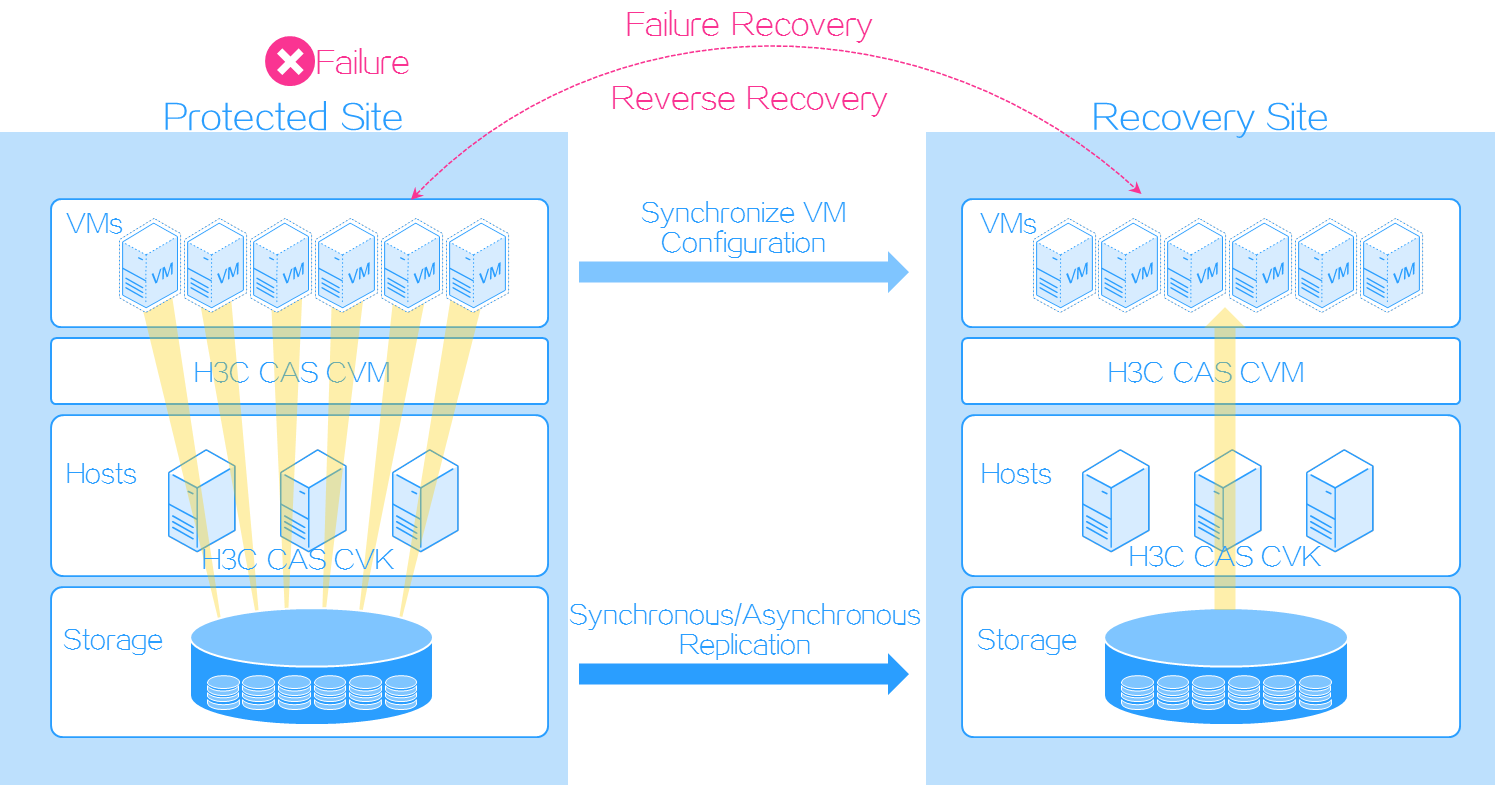
CAS CVM ensures data consistency and service continuity as follows:
At the storage level, DRM backs up data through remote replication between storage arrays.
At the service level, DRM copies configuration of protected VMs from a protected site to a recovery site in each protection group.
When the protected site fails, DRM restores protected VMs on the recovery site by using the data backed up at the storage and service levels based on a recovery plan.
Figure-1 Storage replication-based disaster recovery procedure
Features
Two replication modes
Array-based replication copies data of protected VMs at the storage level to reduce the impact of disaster recovery services on production server performance. You can choose synchronous or asynchronous replication based on your expected RPO and RTO and scenarios.
Support for various disaster recovery scenarios
DRM allows you to simulate disaster recovery without interrupting running services. This mechanism can help you achieve the expected recovery target and decrease RTO. You also can fail over services from a recovery site to a protected site, run recovery as scheduled for maintenance purposes, and fail over services to the recovery site in the event of protected site failure.
One-stop disaster recovery solution
DRM offers unified management of the protected and recovery sites. It can synchronize the disaster recovery configuration on the recovery site with the protected site. You do not need to configure DRM on multiple consoles.
DRM supports one-to-many backup. You can set up multiple recovery sites for a protected site.
Support for a wide range of storage devices
You can use storage arrays from any vendors, as long as they support remote replication and snapshots. With storage arrays that support storage replication adapters (SRAs), DRM can achieve automatic data replication and service failover. For storage arrays that do not support SRAs, you need manually synchronize storage services during service failover.