About elastic IPs
Elastic IP addresses are leased static IP addresses offered by service providers for communication on the Internet. On CloudOS, you can allocate elastic IP addresses to cloud hosts, load balancers, and bare metal nodes and reclaim the elastic IP addresses as needed, and you can set a bandwidth limit on each elastic IP address.
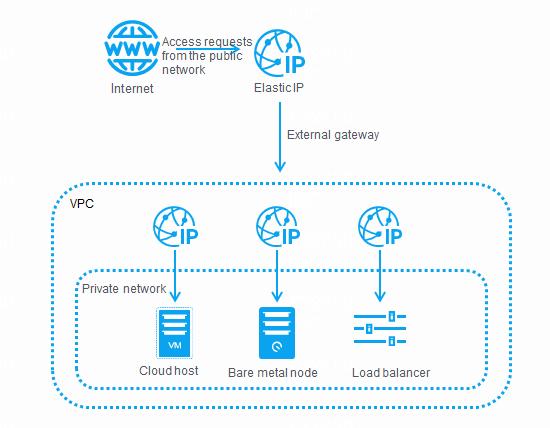
To receive the access requests from the public network, server-side cloud hosts, load balancers, and bare metal nodes must be assigned with elastic IP addresses, and the private networks where they reside must use elastic IP addresses as external gateways.
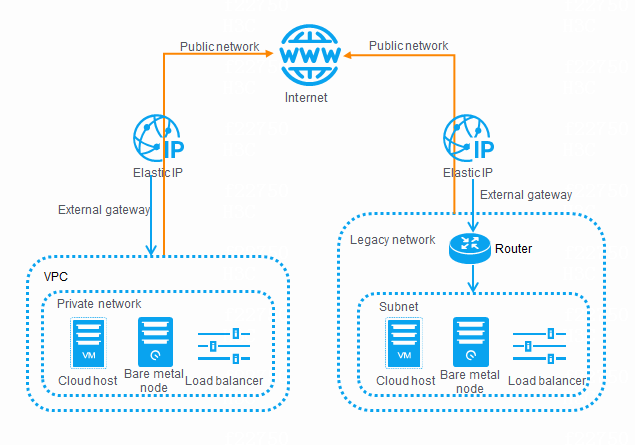
For client-side cloud hosts, load balancers, and bare metal nodes to access the public network, the private networks where they reside must use elastic IP addresses as external gateways.
Concepts
CloudOS manages elastic IP addresses in a hierarchical structure. You must create elastic networks, create subnets on the elastic networks, and add IP address ranges to the elastic subnets. The elastic subnets provide elastic IP addresses for cloud resources that need to communicate with the public network. You can reserve specific IP addresses on an elastic subnet to exclude them from allocation.
Benefits
Decoupling of elastic IP addresses from cloud resources—You can allocate and reclaim elastic IP addresses for cloud resources at will to cope with service changes flexibly.
Bandwidth limit on a per-IP address basis—You can set a bandwidth limit on each elastic IP address to balance bandwidth distribution among services.
Application scenarios
Cloud hosts, load balancers, or bare metal nodes providing services for the public network
If CloudOS cloud hosts, load balancers, or bare metal nodes provide services such as Web, email, or FTP for the public network, you must assign elastic IP addresses to them for them to receive the access requests from the public network.
Cloud hosts, load balancers, or bare metal nodes accessing the public network
If a CloudOS cloud host, load balancer, or bare metal node accesses the public network as a client, you must specify an elastic IP address as an external gateway for the private network where the cloud host, load balancer, or bare metal node resides.
Restrictions and guidelines
The external gateway and the elastic IP of the router or VPC to which the network of the cloud host vNIC or load balancer is attached or belong must meet one of the following requirements:
If the external gateway and the elastic IP belong to the same multi-egress elastic network, the subnets on which the external gateway and the elastic IP reside must have the same external network egress.
The subnets on which the external gateway and the elastic IP reside must have the same external network egress if the following conditions exist:
The router or VPC has a peering connection.
The external gateway and the elastic IP of the router or VPC belong to the same multi-egress elastic network.
Relationship with other services
The following table describes the relationship between elastic IPs and other services. Create cloud services as needed in advance.
|
Service |
Relationship |
|
Cloud host |
Cloud hosts must use elastic IP addresses to receive access requests from the public network. |
|
Load balancer |
Load balancers must use elastic IP addresses to receive access requests from the public network. |
|
VPC/classic network |
Cloud hosts on a VPC or classic network access the public network through the external gateway configured with an elastic IP address on the router attached to the VPC or classic network. |