Application scenarios
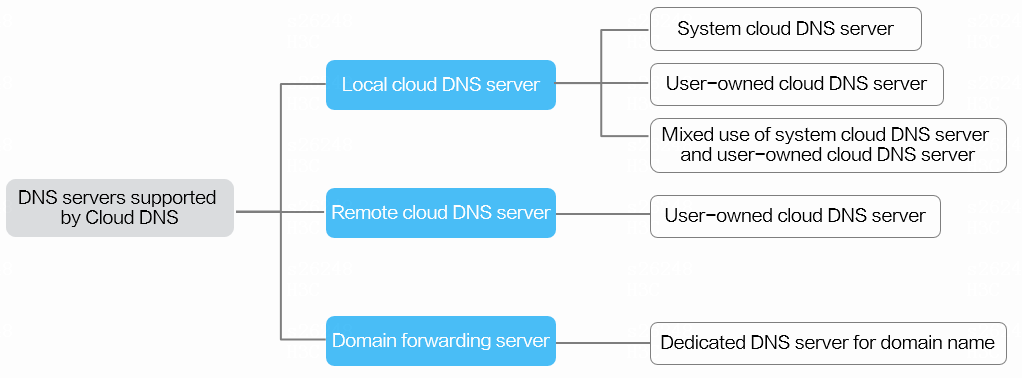
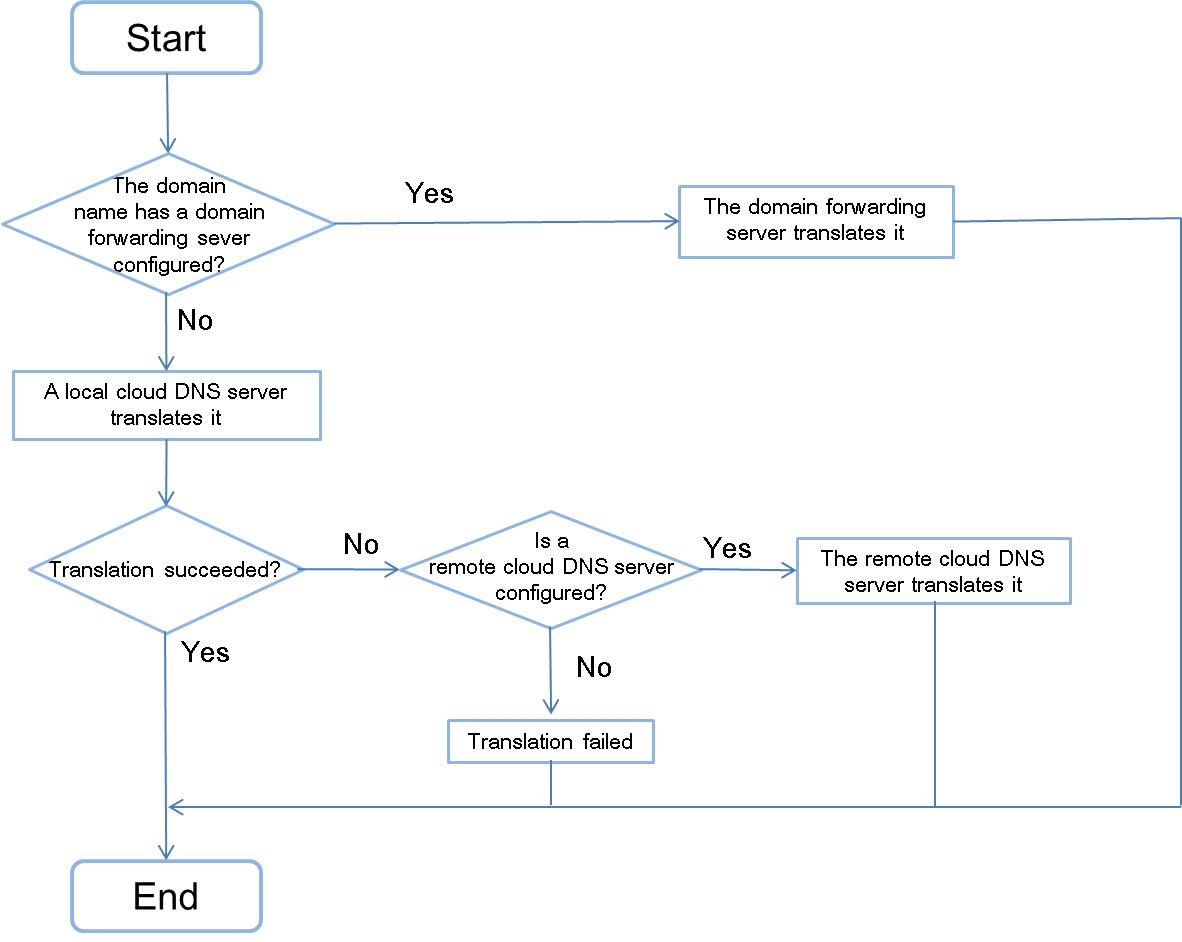
Cloud DNS supports local DNS servers, remote DNS servers, and domain forwarding servers. Local DNS servers include the system cloud DNS server and user-owned DNS servers. Figure-1 and Figure-2 shows the relationships between the cloud DNS servers and how Cloud DNS works.
Remote cloud DNS servers—Resolve the domain names that cannot be resolved by the local cloud DNS server and return the results.
Domain forwarding servers—Forward the domain names to the specified third-party DNS server and return the results.
|
To resolve a public domain name, add a remote DNS server or domain forwarding server that can provide public domain name resolution service. |
System cloud DNS server
The system has a cloud DNS server integrated as a container. After you install and deploy IaaS correctly, the system cloud DNS server integrated with the private domain name resolution feature is responsible for registering and resolving domain names of the resources in the cloud. The IP address of the system cloud DNS server is the system's VIP address, which is used to log in to the system. You can use the integrated system cloud DNS server if you do not own a cloud DNS server.
|
For VMs to access the system cloud DNS server, make sure they can reach the management network of the system. |
User-owned DNS server
You can set up one or multiple cloud DNS servers by yourself. For the system to cooperate with the user-owned DNS servers, you must configure the servers as described in "Configure DNS."
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the user-owned DNS servers meet the following requirements:
The servers must be the bind type.
Ports 953 and 53 are opened.
The servers can communicate with the system over the management network and the VMs that request DNS services.
The servers have the same system time as the system.
The /etc/rndc.key directory of the designate container on the system is copied to the same location on the servers to ensure that the rndc.key directory of the bind program is /etc/rndc.key, and then the bind program is restarted.
The system cloud DNS server does not take effect if you have configured one or multiple user-owned DNS servers. To use the system cloud DNS server, add its IP address (virtual IP address of the system) to cloud DNS server settings.
The system synchronizes the domain records of user-owned DNS servers that have been configured on the system with those configured on the system. When one of the user-owned DNS servers fails, the other DNS servers can ensure service continuity.
If you have configured a remote cloud DNS server, the IP address of the cloud DNS servers is 127.0.0.1 by default.
Add a DNS server
By default, the system uses the built-in DNS server to provide DNS services. You can add DNS servers as needed.
On the top navigation bar, click Resources.
From the left navigation pane, select Network > DNS Configuration.
In the Basic Info area, enter a local or remote DNS server address, and then click Add.
Click Save Configuration.
Domain forwarding server
A domain forwarding server translates a specific second-level domain name. For example, if a domain name has been configured on a cloud DNS server and you do not want to add the server to the system, you can configure that server as a domain forwarding server. Then, the system will direct all requests for the domain name to the domain forwarding server for translation. For more information about the configuration procedure, see "Configure DNS."
Create a DNS forwarding service
To specify a particular DNS server to provide resolution service for a specific subdomain, create a DNS forwarding service for that subdomain. For example, you can configure a DNS forwarding service to forward all requests for resolving text.text to the DNS server at 172.19.18.180.
|
If you have configured a DNS forwarding service, the IP address of the cloud DNS servers is 127.0.0.1 by default. |
On the top navigation bar, click Resources.
From the left navigation pane, select Network > DNS Configuration.
In the Domain Forwarding Service Configuration area, click Create.
Enter the subdomain name and add the IP address of the remote DNS server for resolution of that subdomain name.
Subdomain—A string of 3 to 253 characters. A domain of each level must be a string of 1 to 36 characters that contains digits, letters, underlines, hyphens, and must start with a letter or digit and end with a letter, digit, or dot. You must specify at least a two-level domain name.
DNS Servers—Enter the IP address of the remote DNS server, and then click Add.
Click OK.