CVM stateful failover
About CVM stateful failover
For high availability, you can set up a stateful failover system for CVM with two hosts to prevent hardware or software failure from interrupting services. In the stateful failover system, one host is placed in primary state to provide services, and the other host is placed in backup state as a standby. The hosts synchronize data in real time to maintain configuration consistency. When the primary host fails, the backup host takes over automatically to ensure service continuity for CVM.
Mechanisms
A CVM stateful failover system relies on data replication through Distributed Replicated Block Device (DRBD) to synchronize data between the primary and backup CVM hosts in the system. When the primary CVM host has data changes, the backup CVM host synchronizes its data with the primary CVM host in real time to ensure management data consistency.
In E0523 and later, the CVM master slave daemon (CMSD) controls primary/backup switchover. The major functions of CMSD include the following:
Cluster communication by using Corosync, Pacemaker, and Glue.
Corosync is part of the cluster management suite. When transmitting data, Corosync defines how and by using what protocol data is transmitted in a simple configuration file.
Pacemaker is an open source high-availability cluster resource manager located in the resource manager and resource agent tier of the HA cluster architecture. Pacemaker works as the communication layer to offer relation management, heartbeat engine, and heartbeat detection services.
Management of the stateful failover service, such as enabling or disabling this service or performing primary/backup switchover.
Automatic service failover upon network or host failure.
|
The stateful failover mechanisms in a CVM software version earlier than E0523 are different than E0523 and later. |
Quorum modes
If the primary and backup CVM hosts fail to communicate with each other but have reachability to external networks, the quorum mechanism operates to handle the issue. CVM supports the following quorum modes:
Advanced quorum—A host installed with CMSD acts as a quorum host. Typically, the quorum host is a CVK host managed by the CAS platform that manages the stateful failover system. The primary and backup CVM hosts send their status to the quorum host, and the quorum host determines their roles based on the status information and sends the result back to them.
Ping quorum—Two IP addresses are specified as quorum IP addresses. The primary and backup CVM hosts ping the quorum IP addresses simultaneously to test network connectivity.
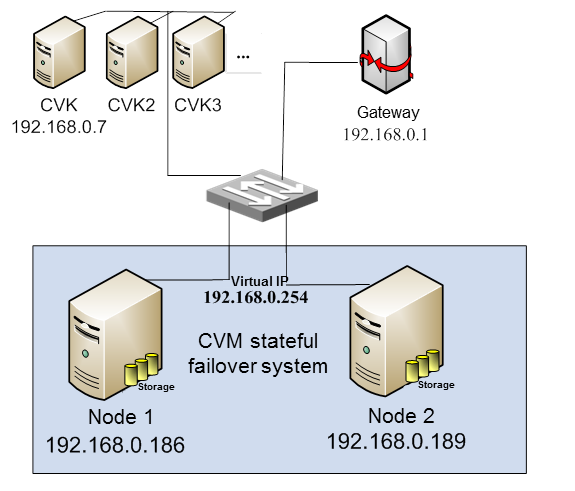
Network diagram
Figure-1 shows a typical stateful failover system network.
Node 1 and Node 2 are the CVM hosts that form the stateful failover system.
CAS runs on multiple CVK hosts and the stateful failover system.
Figure-1 Stateful failover system
In E0523 and later, the stateful failover system contains the following nodes:
Primary and backup nodes with CMSD installed.
Quorum nodes.
For advanced quorum, the quorum node is a CVK host managed by the CAS platform that runs on the primary and backup nodes or a node with CMSD installed.
For ping quorum, the quorum nodes are switches or routers pingable to the primary and backup nodes.
Abbreviations
|
Abbreviation |
Full spelling |
|
CVM |
Cloud Virtualization Manager |
|
CVK |
Cloud Virtualization Kernel |
|
DRBD |
Distributed Replicated Block Device |
|
CMSD |
CVM Master Slave Daemon |