Configuration procedure
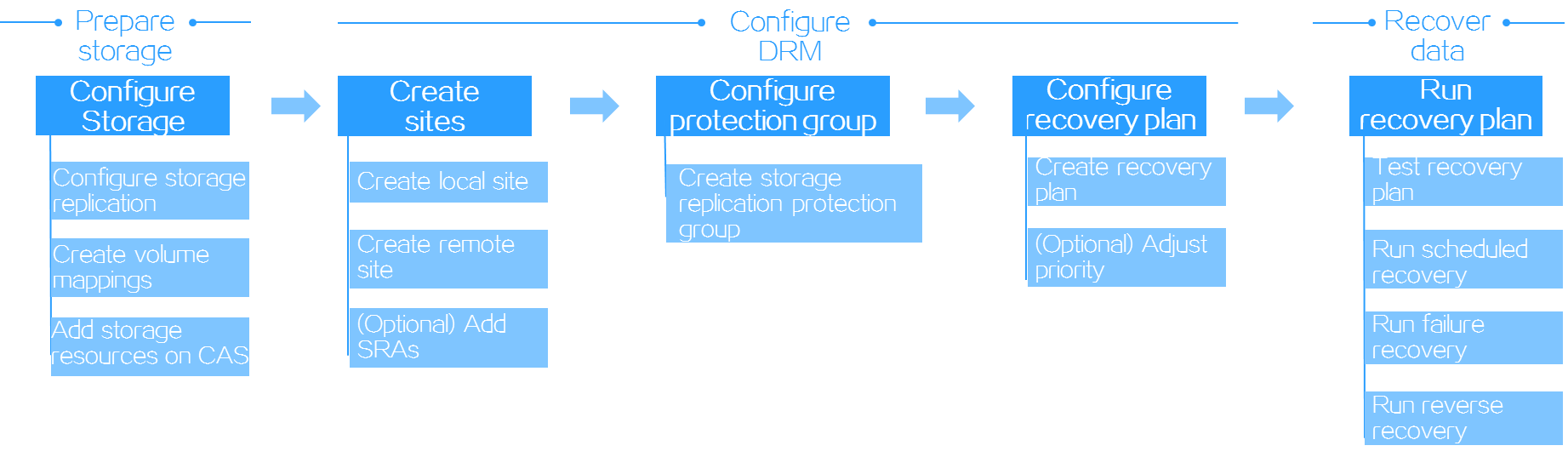
It shows the general configuration procedures for storage replication-based disaster recovery. For more information about the configuration procedures, see "Disaster recovery preparations", "DRM tasks", and "Disaster recovery scenarios".
Figure-1 Configuration procedure for storage replication-based disaster recovery
Disaster recovery preparations
Before you configure storage replication-based disaster recovery, perform the following tasks:
Configure remote replication and volume mappings for storage arrays.
Attach volumes to hosts on CAS.
DRM tasks
Configuring sites
On either the protected site or recovery site, configure a local site and a remote site on CAS. You must add storage array managers when creating sites if storage arrays support SRAs.
Configuring a protection group
A protection group protects a set of VMs or bare metal servers. A protection group protects a set of VMs that use the same storage pool (corresponds to one or multiple LUNs on a storage array) based on a protection policy. It replicates the VM data stored on a LUN on the local storage array to a LUN on a remote storage array through array-based replication.
When you configure a storage replication protection group, you must specify the protected and recovery sites, original and target host pools, and resource mappings. Resource mapping relations associate the resources used by the protected VMs on the protected site with the sources on the recovery site. When VMs are recovered on the recovery site, the resources they use are automatically replaced with the resources of the recovery site. You can configure vSwitch, port profile, and storage (LUN) mappings.
After you create a protection group, CAS automatically synchronizes VM data. In the homogeneous clouds scenario, you also can manually synchronize VM data before failover.
Configuring a recovery plan
DRM allows you to customize disaster recovery settings by creating recovery plans on a per-protection group basis. When a recovery plan is executed, DRM automatically restores protected objects on the recovery site.
Disaster recovery scenarios
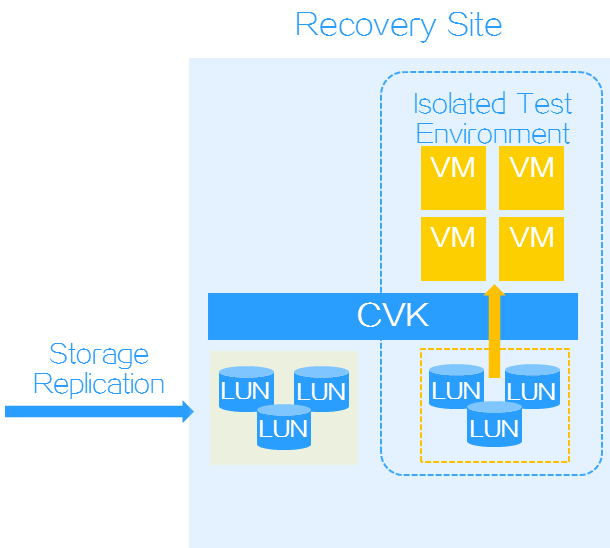
Recovery plan test
DRM allows you to test whether a recovery plan operates correctly by failing over protected objects based on the recovery plan to an isolated test environment on the recovery site without interrupting services. You must manually finish a recovery plan test to clear the environment and restore the state of the recovery plan to Ready.
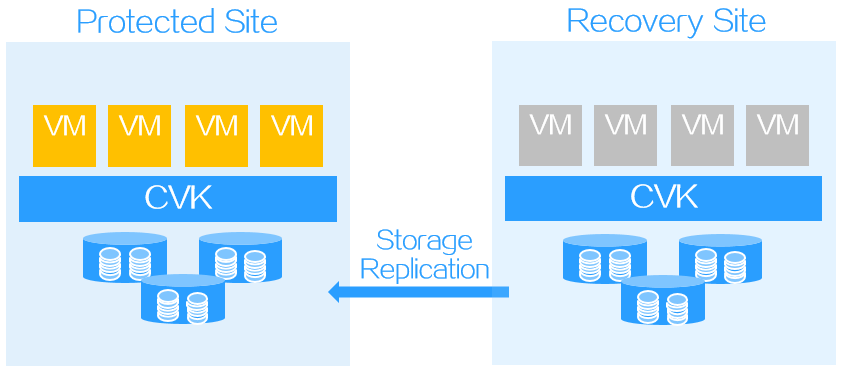
In storage replication-based disaster recovery, VMs are attached to the LUNs on the recovery site.
Figure-2 Recovery plan test for storage replication-based disaster recovery
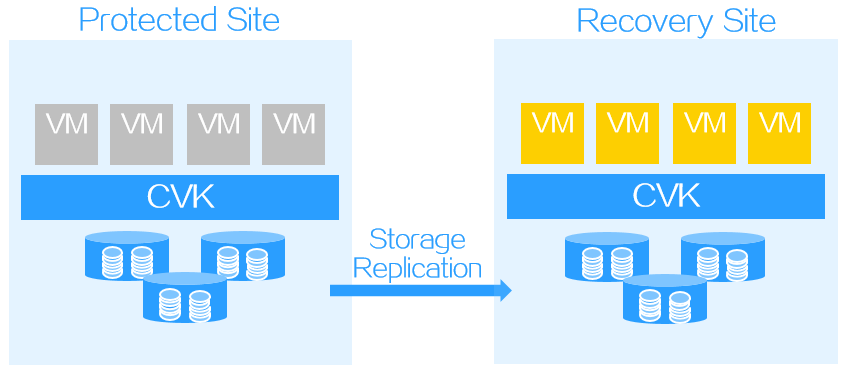
Scheduled recovery
A scheduled recovery resumes protected objects on the recovery site for regular maintenance of the protected site.
Figure-3 Scheduled recovery
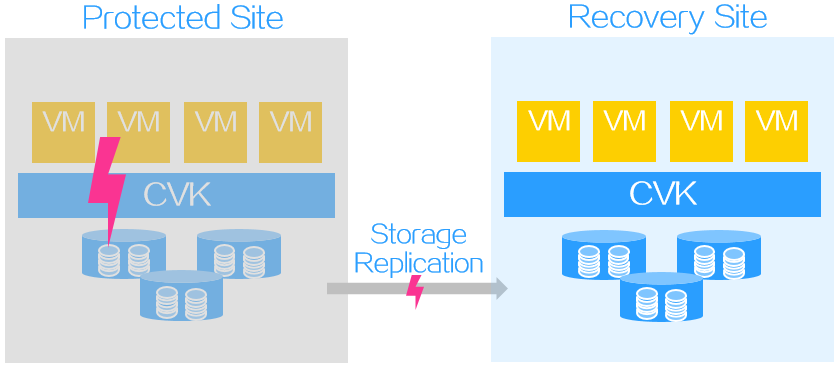
Failure recovery
Failure recovery restores protected objects on the recovery site based on a recover plan to reduce the service interruption time when the protected site fails.
For storage replication-based disaster recovery, the RPO is determined by the replication mode.
For asynchronous replication, the RPO is not 0 when failover recovery is executed.
For synchronous replication, the RPO is 0 when failover recovery is executed.
Figure-4 Failure recovery
Reverse recovery
Storage replication-based disaster recovery can fall back VMs from a recovery site to a protected site when the protected site recovers from failure.
Figure-5 Reverse recovery