Multitenancy management
Multitenancy planning
In cloud computing, a tenant can be an organization, a department within an organization, or an individual. You can deploy UIS Cloud in a multitenancy environment for hierarchical resource management. UIS Cloud assigns resources on a per-tenant basis. Before you create a multitenancy plan, be familiar with the following concepts:
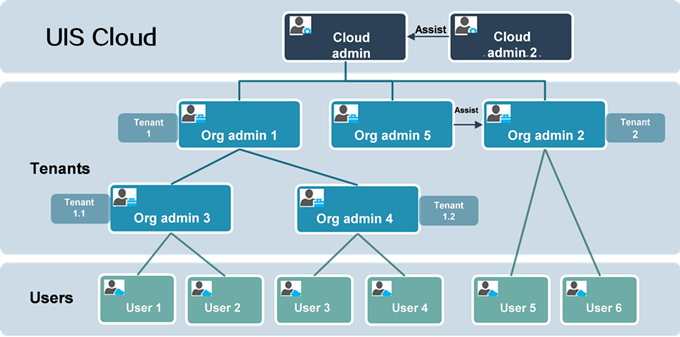
Organization—Each organization represents a group of users. You can create an organization for each tenant. An organization can contain suborganizations. In ClouOS for UIS, the top organization is the private cloud, which is managed by the cloud administrator. An organization hierarchy can contain up to five levels of organizations.
Role—Each role represents a set of permissions and privileges. You control the access of users to the system and resources by assigning roles to them depending on their job responsibilities. By default, UIS Cloud has the following predefined roles:
Cloud administrator.
Organization administrator.
Common user.
Auditor.
User—A user represents anyone that can access the system to manage or use cloud resources. Each user must belong to an organization and be assigned a role to access a set of system functionalities or cloud resources.
A multitenancy plan must contain the following information:
The relationships between organizations.
Assignment of resource quotas, availability zones (AZs), and IP subnets to each organization.
Assignment of users to organizations.
User role assignment.
For example, a company is typically the root organization in UIS Cloud. You create a suborganization for each of its business units, and assign the employees of the business units to their respective suborganizations as users. The IT administrator of the company acts as the cloud administrator to manage all IT resources for the organization and each suborganization has an organization administrator to manage the IT resources assigned to them.
Figure-1 Organization structure in UIS Cloud
Resource quota assignment
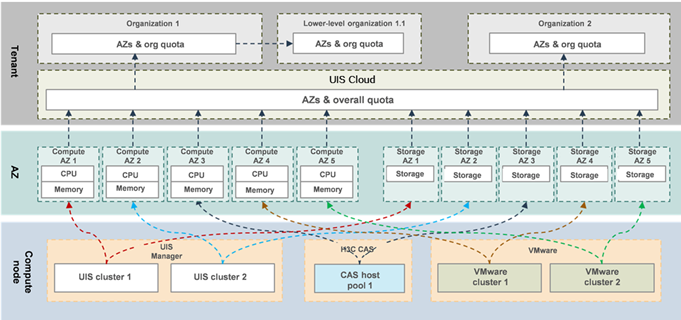
UIS Cloud abstracts managed resources as compute and storage AZs for assignment to organizations. The resource quotas assigned to an organization determine the total amount of resources (for example, CPU cores, memory, and storage) available to users in that organization. The resource AZs assigned to a lower-level organization must be a subset of AZs assigned to its higher-level organization. The sum of resource quotas assigned to all lower-level organizations of an organization cannot exceed the resource quotas assigned to that organization.
Figure-2 Organization-based resource quota and physical resource assignment mappings
Role-based hierarchical user management
UIS Cloud has a predefined private cloud for the top organization and a predefined cloud administrator account with a username of admin. UIS Cloud has the following user roles:
Cloud administrator.
Organization administrator.
Common user.
Auditor.
Each role represents a set of privileges and permissions. Assign users one of these roles depending on their job responsibilities.
Cloud administrator
A cloud administrator has full access to all system functionalities and resources in the system. A user must have this role to manage the system and perform cloud-wide organization and resource management tasks.
Organization administrator
An organization administrator has access to all system functionalities and resources specific to an organization for management of users and resources assigned to that organization. For example, organization administrators create suborganizations, create users, and assign roles and privileges to those users in their managed organizations. They also manage resource quotas, review resource approval workflows, and monitor services and alarms in their respective organizations.
Common user
Common users have access to cloud services and resources assigned to them as well as notifications related to them. In addition, they have read access to shared resources in their respective organizations.
Auditor
An auditor has only read access to the operation log in the system for user behavior auditing.
Multitenancy scenario
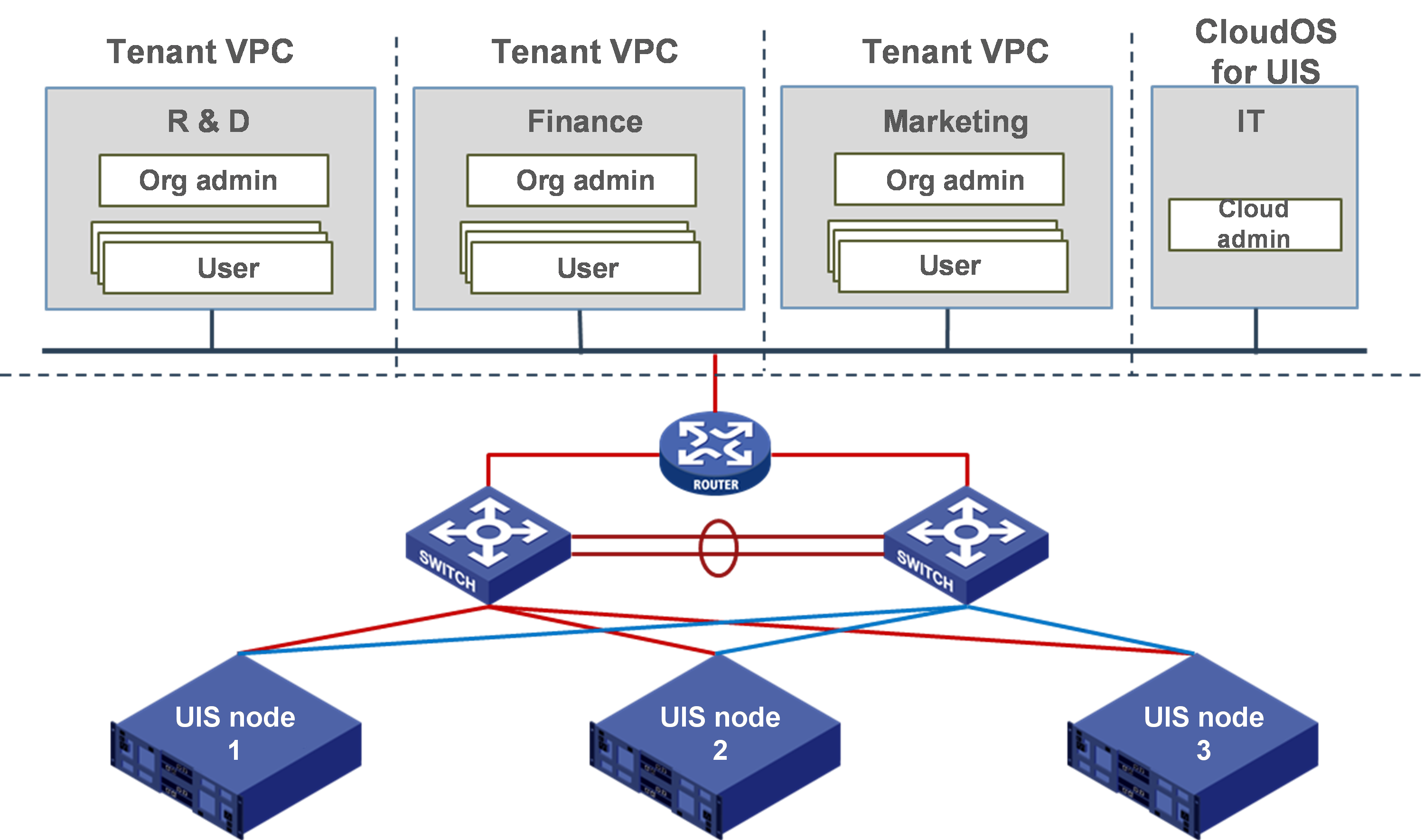
Figure-3 shows a typical deployment of UIS Cloud in a multitenancy environment.
Figure-3 Typical deployment of UIS Cloud in a multitenancy environment
The following is the generic deployment procedure:
Deploy three UIS servers installed with UIS Manager Standard Edition at the infrastructure layer.
Deploy UIS Cloud on top of UIS Manager at a click.
The IT administrator of the company logs in to UIS Cloud as a cloud administrator to perform the following tasks as planned:
Create organizations. For example, create three organizations, one for the R&D department, one for the financial department, and one for the marketing department.
Assign AZs and resource quotas to each organization.
Create an organization administrator for each organization.
The administrator of each organization performs the following tasks based on the assigned resources:
Configure the network and network services for the organization, including IP assignment, subnetting, firewall, and image services.
Create users in the organization.
The common users create workflows to request services such as cloud hosts and cloud disks.
The resources, network, and security configuration are isolated between organizations.