- Table of Contents
-
- 15-WLAN Configuration Guide (FAT AP)
- 00-Preface
- 01-Compatibility of hardware and AP functionality
- 02-Radio management configuration
- 03-WLAN access configuration
- 04-WLAN security configuration
- 05-WLAN authentication configuration
- 06-WLAN QoS configuration
- 07-WLAN load balancing configuration
- 08-Band navigation configuration
- 09-WLAN multicast optimization configuration
- Related Documents
-
| Title | Size | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 03-WLAN access configuration | 252.98 KB |
Whitelist- and blacklist-based access control
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WLAN access
Configuring a service template
Configuring a description for a service template
Setting the maximum number of associated clients for a service template
Binding a service template to a radio interface
Specifying the method for APs to process traffic from unknown clients
Specifying the Web server to which client information is reported
Enabling generation of client logs in the specified format
Setting the idle period before client reauthentication
Configuring client maintenance
Setting the client idle timeout
Performing a wireless link quality test
Configuring client association ratio optimization
Configuring client access control
Adding a client to the whitelist
Adding a client to the static blacklist
Configuring the dynamic blacklist
Configuring ACL-based access control
Disabling an AP from responding to broadcast probe requests
Enabling SNMP notifications for WLAN access
Display and maintenance commands for WLAN access
WLAN access configuration examples
Example: Configuring WLAN access
Example: Configuring whitelist-based access control
Example: Configuring static blacklist-based access control
Configuring WLAN access
About WLAN access
Wireless access is provided by APs deployed at the edge of a wired network. The APs connect to the uplink through wired connections and provide wireless access services to downlink clients.
WLAN access process
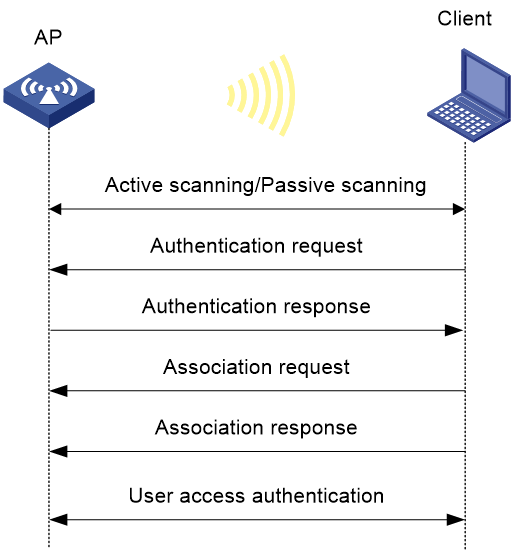
A wireless client can access a WLAN only when it completes the scanning, link layer authentication, association, and WLAN authentication processes.
For more information about data link layer authentication, see "Configuring WLAN security." For more information about WLAN authentication, see "Configuring WLAN authentication."
Figure 1 WLAN access process
Scanning
Active scanning
A wireless client periodically scans surrounding wireless networks by sending probe requests. It obtains network information from received probe responses. Based on whether a probe request carries an SSID, active scanning can be divided into the following types:
· Active scanning of all wireless networks.
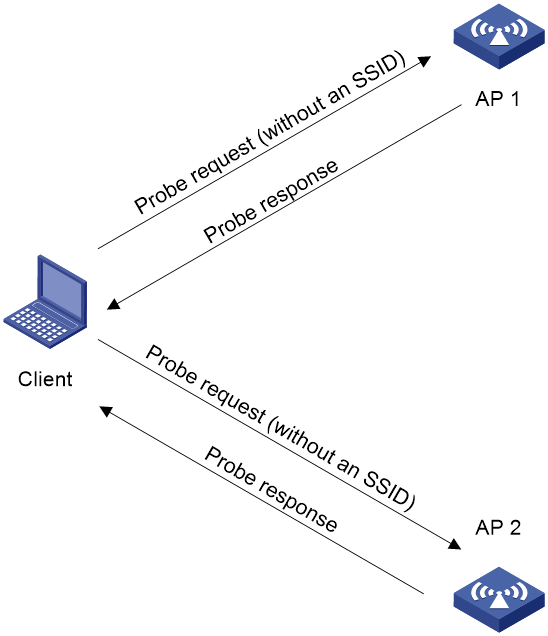
As shown in Figure 2, the client periodically sends a probe request on each of its supported channels to scan wireless networks. APs that receive the probe request send a probe response that carries the available wireless network information. The client associates with the optimal AP.
Figure 2 Scanning all wireless networks
· Active scanning of a specific wireless network.
As shown in Figure 3, the client periodically sends a probe request carrying the specified SSID or the SSID of the wireless network it has been associated with. When an AP that can provide wireless services with the specified SSID receives the probe request, it sends a probe response.
Figure 3 Scanning a specific wireless network
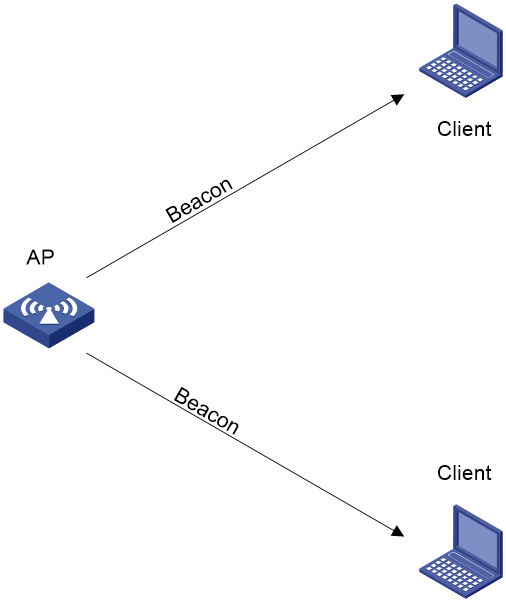
Passive scanning
As shown in Figure 4, the clients periodically listen for beacon frames sent by APs on their supported channels to get information about surrounding wireless networks. Then the clients select an AP for association. Passive scanning is used when clients want to save power.
Association
A client sends an association request to the associated AP after passing date link layer authentication. Upon receiving the request, the AP determines the capability supported by the wireless client and sends an association response to the client. Then the client is associated with the AP.
Client access control
The following client access control methods are available:
· Whitelist- and blacklist-based access control—Uses the whitelist and blacklists to control client access.
· ACL-based access control—Uses ACL rules bound to APs or service templates to control client access.
Whitelist- and blacklist-based access control
You can configure the whitelist or blacklists to filter frames from clients for client access control.
Whitelist-based access control
The whitelist contains the MAC addresses of all clients allowed to access the WLAN. Frames from clients not in the whitelist are discarded. This list is manually configured.
Blacklist-based access control
The following blacklists are available for access control:
· Static blacklist—Contains the MAC addresses of clients forbidden to access the WLAN. This list is manually configured.
· Dynamic blacklist—Contains the MAC addresses of clients forbidden to access the WLAN. An AP adds the MAC address of a client forbidden to access the WLAN to the list when WIPS is configured or when URL redirection is enabled for WLAN MAC authentication clients. The entries in the list are removed when the aging time expires.
Working mechanism
When the AP receives an association request, the AP performs the following operations to determine whether to permit the client:
1. Searches the whitelist:
¡ If the client MAC address does not match any entry in the whitelist, the client is rejected.
¡ If a match is found, the client is permitted.
2. Searches the static and dynamic blacklists if no whitelist entries exist:
¡ If the client MAC address matches an entry in either blacklist, the client is rejected.
¡ If no match is found, or no blacklist entries exist, the client is permitted.
Figure 5 Whitelist- and blacklist-based access control
ACL-based access control
This feature controls client access by using ACL rules bound to an AP or a service template.
Upon receiving an association request from a client, the device performs the following actions:
· Allows the client to access the WLAN if a match is found and the rule action is permit.
· Denies the client's access to the WLAN if no match is found or the matched rule has a deny statement.
Restrictions: Hardware compatibility with WLAN access
For information about MSR routers that can offer WLAN services as fat APs, see "Compatibility of hardware and AP functionality."
WLAN access tasks at a glance
To configure WLAN access, perform the following tasks:
1. Configuring wireless services
¡ Configuring a service template
¡ (Optional.) Configuring a description for a service template
¡ (Optional.) Setting the maximum number of associated clients for a service template
¡ Binding a service template to a radio interface
2. (Optional.) Specifying the method for APs to process traffic from unknown clients
3. (Optional.) Configuring client management
¡ Specifying the Web server to which client information is reported
¡ Enabling generation of client logs in the specified format
¡ Setting the idle period before client reauthentication
4. (Optional.) Configuring client maintenance
¡ Setting the client idle timeout
¡ Configuring client keepalive
¡ Performing a wireless link quality test
¡ Configuring client association ratio optimization
5. (Optional.) Configuring client access control
¡ Adding a client to the whitelist
¡ Adding a client to the static blacklist
¡ Configuring the dynamic blacklist
¡ Configuring ACL-based access control
6. (Optional.) Disabling an AP from responding to broadcast probe requests
7. (Optional.) Setting the LED lighting mode
8. (Optional.) Enabling SNMP notifications for WLAN access
9. (Optional.) Enabling smart client access
Configuring wireless services
Configuring a service template
About this task
A service template defines a set of wireless service attributes, such as SSID and authentication method.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Create a service template.
wlan service-template service-template-name
By default, no service template exists.
3. (Optional.) Assign clients coming online through the service template to the specified VLAN.
vlan vlan-id
By default, clients are assigned VLAN 1 after coming online through a service template.
Configuring a description for a service template
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Configure a description for the service template.
description text
By default, no description is configured for a service template.
Setting an SSID
About this task
APs broadcast SSIDs in beacon frames for clients to discover them. When a BSS is unavailable or when you do not want clients to discover the BSS, you can enable SSID-hidden. With SSID-hidden enabled, the BSS hides its SSID in beacon frames and does not respond to broadcast probe requests. A client must send probe requests with the specified SSID to access the WLAN. This feature can protect the WLAN from being attacked.
When the number of clients associated with an AP reaches the upper limit, the AP automatically hides its SSIDs in beacon frames, and other clients cannot discover and associate with the AP. For these clients to discover the AP, you can configure the SSID broadcast feature. However, these clients still cannot associate with the AP.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Set an SSID for the service template.
ssid ssid-name
By default, no SSID is set for a service template.
4. (Optional.) Enable SSID-hidden in beacon frames.
beacon ssid-hide
By default, SSIDs are not hidden in beacon frames.
5. (Optional.) Enable SSID broadcast in beacon frames.
beacon ssid-advertise
By default, an AP hides SSIDs in beacon frames when the maximum number of associated clients is reached.
Setting the maximum number of associated clients for a service template
About this task
Perform this task to limit the associated client quantity to avoid overload. With this feature configured, new clients cannot access the WLAN and the SSID is hidden when the maximum number is reached.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Set the maximum number of associated clients for the service template.
client max-count max-number
By default, the number of associated clients for a service template is not limited.
Enabling a service template
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable the service template.
service-template enable
By default, a service template is disabled.
Binding a service template to a radio interface
Restrictions and guidelines
You can bind a maximum of 16 service templates to a radio interface.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter WLAN-Radio interface view.
interface wlan-radio interface-number
3. Bind a service template to the radio interface.
service-template service-template-name
By default, no service template is bound to a radio interface.
Specifying the method for APs to process traffic from unknown clients
About this task
Perform this task to configure APs using the specified service template to drop data packets from unknown clients and deauthenticate these clients or to drop the packets only.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Specify the method for APs to process traffic from unknown clients.
unknown-client [ deauthenticate | drop ]
By default, APs drop packets from unknown clients and deauthenticate these clients.
Configuring client management
Enabling quick association
About this task
Enabling band navigation might affect client association efficiency. For delay-sensitive services or in an environment where band navigation is not needed, you can enable quick association for a service template.
Quick association disables band navigation on clients associated with the service template. The device will not perform band navigation even if the feature is enabled in the WLAN.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable quick association.
quick-association enable
By default, quick association is disabled.
Specifying the Web server to which client information is reported
About this task
Perform this task to enable the device to report client information, such as client MAC address, associated AP, and association time, to the specified Web server through HTTP. The Web server accepts client information only when the server's host name, port number, and path are specified.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Specify the host name and port number of the Web server.
wlan web-server host host-name port port-number
By default, the host name and port number of the Web server are not specified.
3. Specify the path of the Web server.
wlan web-server api-path path
By default, the path of the Web server is not specified.
4. (Optional.) Set the maximum number of client entries that can be reported at a time.
wlan web-server max-client-entry number
By default, a maximum of ten client entries can be reported at a time.
Enabling generation of client logs in the specified format
About this task
The device supports client logs in the following formats:
· H3C—Logs AP name, radio ID, client MAC address, SSID, BSSID, and client online status. By default, the device generates client logs only in H3C format.
· Normal—Logs AP MAC address, AP name, client IP address, client MAC address, SSID, and BSSID.
· Sangfor—Logs AP MAC address, client IP address, and client MAC address.
This feature enables the device to generate client logs in normal or sangfor format and send the logs to the information center. Log destinations are determined by the information center settings. For more information about the information center, see Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
This feature does not affect generation of client logs in the H3C format.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable the device to generate client logs in the specified format.
customlog format wlan { normal | sangfor }
By default, the device generates client logs only in the H3C format.
Setting the idle period before client reauthentication
About this task
When URL redirection for WLAN MAC authentication is enabled, an AP redirects clients whose information is not recorded on the RADIUS server to the specified URL for Web authentication. Clients passing Web authentication are logged off and must perform MAC reauthentication to come online. However, MAC reauthentication fails if the IP addresses assigned to the clients have not expired.
Perform this task to add these clients to the dynamic blacklist for the specified idle period after they pass Web authentication to reduce reauthentication failures.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the idle period before client reauthentication.
wlan client reauthentication-period [ period-value ]
By default, the idle period is 10 seconds.
Configuring client maintenance
Setting the client idle timeout
About this task
If an online client does not send any frames to the associated AP before the client idle timeout timer expires, the AP logs off the client.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the client idle timeout.
wlan client idle-timeout timeout
By default, the client idle timeout is 3600 seconds.
Configuring client keepalive
About this task
This feature enables an AP to send keepalive packets to clients at the specified interval to determine whether the clients are online. If the AP does not receive any replies from a client within three keepalive intervals, it logs off the client.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enable client keepalive.
wlan client keep-alive enable
By default, client keepalive is disabled.
3. Set the client keepalive interval.
wlan client keep-alive interval interval
By default, the client keepalive interval is 300 seconds.
Performing a wireless link quality test
About this task
This feature enables an AP to test the quality of the link to a wireless client. The AP sends empty data frames to the client at each supported rate. Then it calculates link quality information such as RSSI, packet retransmissions, and RTT based on the responses from the client.
The timeout for a wireless link quality test is 10 seconds. If the wireless link test is not completed before the timeout expires, test results cannot be obtained.
Procedure
To perform a wireless link quality test, execute the wlan link-test mac-address command in user view.
Setting the NAS ID
About this task
A network access server identifier (NAS ID) or network access server port identifier (NAS port ID) identifies the network access server of a client and differentiates the source of client traffic.
Restrictions and guidelines
If you specify a NAS ID when binding a service template to a radio, the radio uses the NAS ID specified for the service template.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the format of NAS port IDs for wireless clients.
wlan nas-port-id format { 2 | 4 }
By default, clients use format 2 to generate NAS port IDs.
3. Enter global configuration view.
wlan global-configuration
4. Set the NAS ID.
nas-id nas-id
By default, no NAS ID is set.
Setting the NAS port type
About this task
RADIUS requests carry the NAS port type attribute to indicate type of the access port for 802.1X and MAC authentication clients.
Restrictions and guidelines
Make sure the service template is disabled before you perform this task.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template
3. Set the NAS port type.
nas-port-type value
By default, the NAS port type is WLAN-IEEE 802.11 with a code value of 19.
Configuring client association ratio optimization
About this task
This feature enables the device to recalculate the client association success ratio, association congestion ratio, and abnormal disassociation ratio by using the specified index to get smaller ratio values.
The client association success ratio is the number of successful client associations divided by the total number of client association attempts. The client association congestion ratio is the number of failed client associations caused by AP overloading divided by the total number of client association attempts. The client abnormal disassociation ratio is the number of abnormal disassociations divided by the sum of successful associations and online clients.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter global configuration view.
wlan association optimization value
By default, the index is 0. The device does not optimize client association ratios.
Configuring client access control
Adding a client to the whitelist
Restrictions and guidelines
When you add the first client to the whitelist, the system asks you whether to disconnect all online clients. Enter Y at the prompt to configure the whitelist.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Add a client to the whitelist.
wlan whitelist mac-address mac-address
Adding a client to the static blacklist
Restrictions and guidelines
You cannot add a client to both the whitelist and the static blacklist.
If the whitelist and blacklists are configured, only the whitelist takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Add a client to the static blacklist.
wlan static-blacklist mac-address mac-address
Configuring the dynamic blacklist
About this task
The AP adds the MAC address of a client forbidden to access the WLAN to the list when WIPS is configured or when URL redirection is enabled for WLAN MAC authentication clients.
Entries in the dynamic blacklist are removed when the aging timer expires.
Restrictions and guidelines
The configured aging timer takes effect only on entries newly added to the dynamic blacklist.
If the whitelist and blacklists are configured, only the whitelist takes effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the aging timer for dynamic blacklist entries.
wlan dynamic-blacklist lifetime lifetime
By default, the aging timer is 300 seconds.
The aging timer for dynamic blacklist entries takes effect only on rogue client entries.
Configuring ACL-based access control
Restrictions and guidelines
The ACL-based access control configuration takes precedence over the whitelist and blacklist configuration. As a best practice, do not configure both ACL-based access control and whitelist- and blacklist-based access control on the same device.
If the specified ACL contains a deny statement, configure a permit statement for the ACL to permit all clients. If you do not do so, no clients can come online.
This feature supports only Layer 2 ACLs and can only use source MAC address as the match criterion. If you specify an ACL of another type, the configuration does not take effect.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Specify an ACL.
access-control acl acl-number
By default, no ACL is specified.
Disabling an AP from responding to broadcast probe requests
About this task
Broadcast probe requests do not carry any SSIDs. Upon receiving a broadcast probe request, an AP responds with a probe response that carries service information for the AP.
This feature enables clients that send unicast probe requests to the AP to associate with the AP more easily.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Disable the AP from responding to broadcast probe requests.
undo wlan broadcast-probe reply
By default, an AP responds to broadcast probe requests.
Setting the LED lighting mode
About this task
You can configure the LEDs on an AP to flash in the following modes:
· quiet—All LEDs are off.
· awake—All LEDs flash once every minute. Support for this mode depends on the AP model.
· always-on—All LEDs are steady on. Support for this mode depends on the AP model.
· normal—How LEDs flash in this mode varies by AP model. This mode can identify the running status of an AP.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Set the LED flash mode.
wlan led-mode { always-on | awake | normal | quiet }
By default, the LED lighting mode is normal.
Enabling SNMP notifications for WLAN access
About this task
To report critical WLAN access events to an NMS, enable SNMP notifications for WLAN access. For WLAN access event notifications to be sent correctly, you must also configure SNMP as described in Network Management and Monitoring Configuration Guide.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Choose the options to configure as needed:
¡ Enable SNMP notifications for client access.
snmp-agent trap enable wlan client
¡ Enable SNMP notifications for client audit.
snmp-agent trap enable wlan client-audit
By default, SNMP notifications are disabled.
Enabling smart client access
About smart client access
This feature enables H3C wireless clients to access the WLAN automatically when the AKM mode is set to PSK or when the radio is bound to an empty service template.
Procedure
1. Enter system view.
system-view
2. Enter service template view.
wlan service-template service-template-name
3. Enable smart client access.
client smart-access enable
By default, smart client access is disabled.
Display and maintenance commands for WLAN access
Execute display commands in any view and the reset command in user view.
|
Task |
Command |
|
Display WLAN radio interface information. |
display interface wlan-radio [ interface-number ] [ brief ] |
|
Display the number of online clients at the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band. |
display wlan ap all client-number |
|
Display the number of online clients and channel information for each radio. |
display wlan ap all radio client-number |
|
Display blacklist entries. |
display wlan blacklist { dynamic | static } |
|
Display basic service set (BSS) information. |
display wlan bss { all | bssid bssid } [ verbose ] |
|
Display client information. |
display wlan client [ interface wlan-radio interface-number | mac-address mac-address | service-template service-template-name | vlan vlan-id ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display information about client IPv6 addresses. |
display wlan client ipv6 |
|
Display client online duration. |
display wlan client online-duration [ verbose ] |
|
Display client status information. |
display wlan client status [ mac-address mac-address ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display service template information. |
display wlan service-template [ service-template-name ] [ verbose ] |
|
Display client statistics. |
display wlan statistics client [ mac-address mac-address ] |
|
Display client connection history. |
display wlan statistics connect-history service-template service-template-name |
|
Display service template statistics. |
display wlan statistics service-template service-template-name |
|
Display whitelist entries. |
display wlan whitelist |
|
Log off the specified client or all clients. |
reset wlan client { all | mac-address mac-address } |
|
Remove the specified client or all clients from the dynamic blacklist. |
reset wlan dynamic-blacklist [ mac-address mac-address ] |
|
Clear client statistics. |
reset wlan statistics client { all | mac-address mac-address } |
|
Clear service template statistics. |
reset wlan statistics service-template service-template-name |
WLAN access configuration examples
Example: Configuring WLAN access
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 6, the switch acts as the DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the AP and the client. The AP provides wireless services with SSID trade-off.
Procedure
# Create service template service1, set the SSID to trade-off, and enable the service template.
<AP> system-view
[AP] wlan service-template service1
[AP-wlan-st-service1] ssid trade-off
[AP-wlan-st-service1] service-template enable
[AP-wlan-st-service1] quit
# Bind service template service1 to WLAN-Radio 0/0.
[AP] interface wlan-radio 0/0
[AP-WLAN-Radio0/0] undo shutdown
[AP-WLAN-Radio0/0] service-template service1
[AP-WLAN-Radio0/0] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that the SSID is trade-off, and the service template is enabled.
[AP] display wlan service-template verbose
Service template name : service1
Description : Not configured
SSID : trade-off
SSID-hide : Disabled
User-isolation : Disabled
Service template status : Enabled
Maximum clients per BSS : Not configured
Frame format : Dot3
Seamless roam status : Disabled
Seamless roam RSSI threshold : 50
Seamless roam RSSI gap : 20
VLAN ID : 3
AKM mode : Not configured
Security IE : Not configured
Cipher suite : Not configured
TKIP countermeasure time : 0 sec
PTK life time : 43200 sec
PTK rekey : Enabled
GTK rekey : Enabled
GTK rekey method : Time-based
GTK rekey time : 86400 sec
GTK rekey client-offline : Disabled
WPA3 status : Disabled
PPSK : Disabled
PPSK Fail Permit : Disabled
Enhance-open status : Enabled
Enhanced-open transition-mode service-template : N/A
User authentication mode : Bypass
Intrusion protection : Disabled
Intrusion protection mode : Temporary-block
Temporary block time : 180 sec
Temporary service stop time : 20 sec
Fail VLAN ID : Not configured
Critical VLAN ID : Not configured
802.1X handshake : Disabled
802.1X handshake secure : Disabled
802.1X domain : my-domain
MAC-auth domain : Not configured
Max 802.1X users per BSS : 4096
Max MAC-auth users per BSS : 4096
802.1X re-authenticate : Disabled
Authorization fail mode : Online
Accounting fail mode : Online
Authorization : Permitted
Key derivation : SHA1
PMF status : Disabled
Hotspot policy number : Not configured
Forwarding policy status : Disabled
Forwarding policy name : Not configured
Forwarder : AP
FT status : Disabled
QoS trust : Port
QoS priority : 0
# Associate the client with the fat AP. (Details not shown.)
# Verify that the client can access the WLAN.
[AP] display wlan client service-template service1
Total number of clients: 1
MAC address Username AP name RID IP address IPv6 address VLAN
0023-8933-223b N/A fatap 1 3.0.0.3 3
Example: Configuring whitelist-based access control
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 7, configure the whitelist to permit only the client whose MAC address is 0000-000f-1211 to access the WLAN.
Procedure
# Add MAC address 0000-000f-1211 to the whitelist.
<AP> system-view
[AP] wlan whitelist mac-address 0000-000f-1211
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that MAC address 0000-000f-1211 is in the whitelist.
<AP> display wlan whitelist
Total number of clients: 1
MAC addresses:
0000-000f-1211
Example: Configuring static blacklist-based access control
Network configuration
As shown in Figure 8, configure the static blacklist to forbid the client whose MAC address is 0000-000f-1211 to access the WLAN.
Procedure
# Add MAC address 0000-000f-1211 to the static blacklist.
<AP> system-view
[AP] wlan static-blacklist mac-address 0000-000f-1211
Verifying the configuration
# Verify that MAC address 0000-000f-1211 is in the static blacklist.
<AP> display wlan blacklist static
Total number of clients: 1
MAC addresses:
0000-000f-1211