About public IPs
Public IPs are valid static IP addresses for communication on the Internet. Usually, you need to purchase public IPs from the ISP. Public IPs can be bound to or unbound from cloud hosts and load balancers in the system. If a cloud host or load balancer operates as a server to receive access requests from the public network, you need to bind the cloud host or load balancer to a public IP. Besides, you also need to bind the private network of the cloud host or load balancer to a public IP, which is used as the border gateway IP. If a cloud host or load balancer operates only as a client to access the public network, you only need to bind its private network to a public IP to save public IP resources. If no public network communication is needed or some faults occur, you can unbind the public IPs, so that the public IPs can be assigned to other cloud services.
Concepts
Public IP Pools
The public IPs in the system resides in subnets of public IP pools. Before creating a public IP, you need to create a public IP pool, and add subnets in the pool. In a subnet, you need to configure the public IP address ranges available for allocation. You can also configure the reserve IPs, which must belong to a subnet of the public IP pool. Reserved IP addresses will not be allocated to resources.
Prerequisites
Before configuring public IPs, make sure the UIS-Sec component has been installed and the cloud administrator has set the network automation mode to enhanced network mode.
Before creating a public IP, make sure the cloud administrator has created an available public IP pool on the Cloud Services > Network & Security > Public IP Pools page.
To assign a public IP to a cloud host, the network of the vNIC of the cloud host must be attached to a router, and the router's border gateway IP and the public IP must belong to the same public IP pool.
To assign a public IP to a load balancer, the border gateway IP of the router (to which the load balancer is attached) and the public IP must belong to the same public IP pool.
Benefits
Decoupling with cloud resources
The public IPs and cloud resources can be unbound at any time as needed. This allows for flexible adaption to service changes
Application scenarios
Public network access to cloud hosts/load balancers
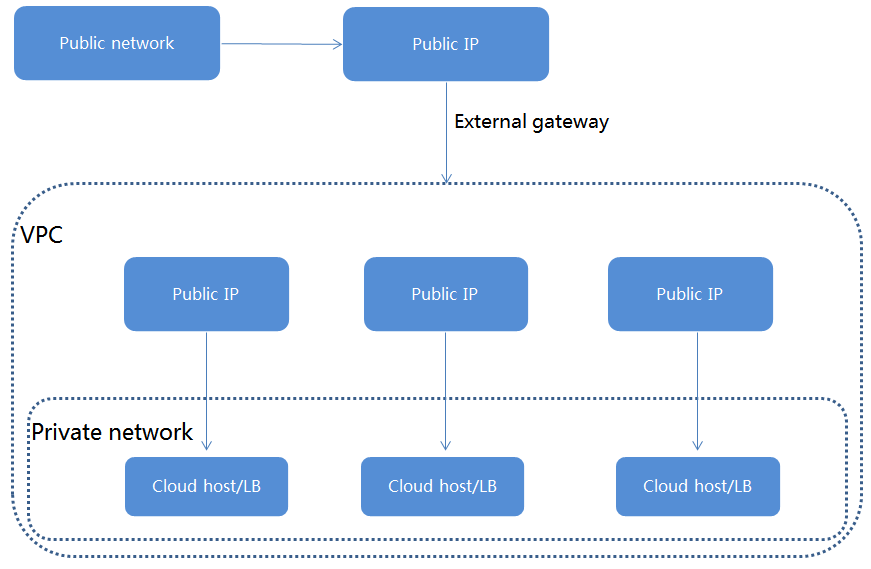
When a cloud host or load balancer needs to provide access services to the public network, for example, as a Web, mail, or FTP server, the cloud host or load balancer must be bound to a public IP.
Figure-1 Public network access to cloud hosts/load balancers
Cloud hosts/load balancers access to the public network
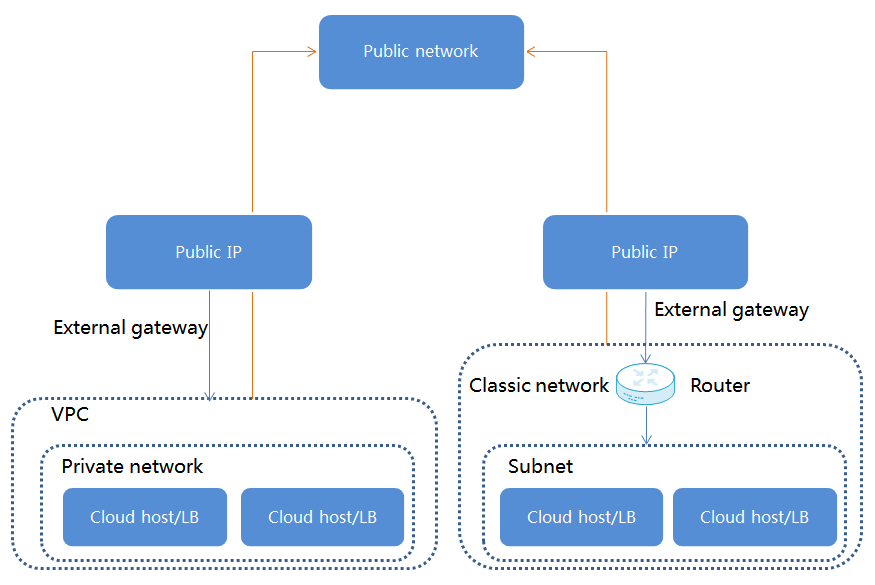
If a cloud host or load balancer operates only as a client to access the public network, you only need to bind its private network to a public IP.
Figure-2 Cloud hosts/load balancers access to the public network
Restrictions and guidelines
A public IP can be assigned to only one cloud host or load balancer.
To assign a public IP to a cloud host, the network of the vNIC of the cloud host must be attached to a router, and the router's border gateway IP and the public IP must belong to the same subnet.
To assign a public IP to a load balancer, the border gateway IP of the router (to which the load balancer is attached) and the public IP must belong to the same network.
Dependencies between public IP and other cloud services
Table-1 shows the dependencies between public IP and other cloud services. Please create corresponding cloud services in advance.
Table-1 Dependencies between public IP and other cloud services
|
Service Name |
Description |
|
Cloud host |
If a cloud host needs to receive access requests from the public network, you need to assign a public IP address to the vNIC of the cloud host. |
|
Load Balancer |
If a load balancer needs to receive access requests from the public network, you need to assign a public IP address to the load balancer. |