Add a VM
On the top navigation bar, click VMs.
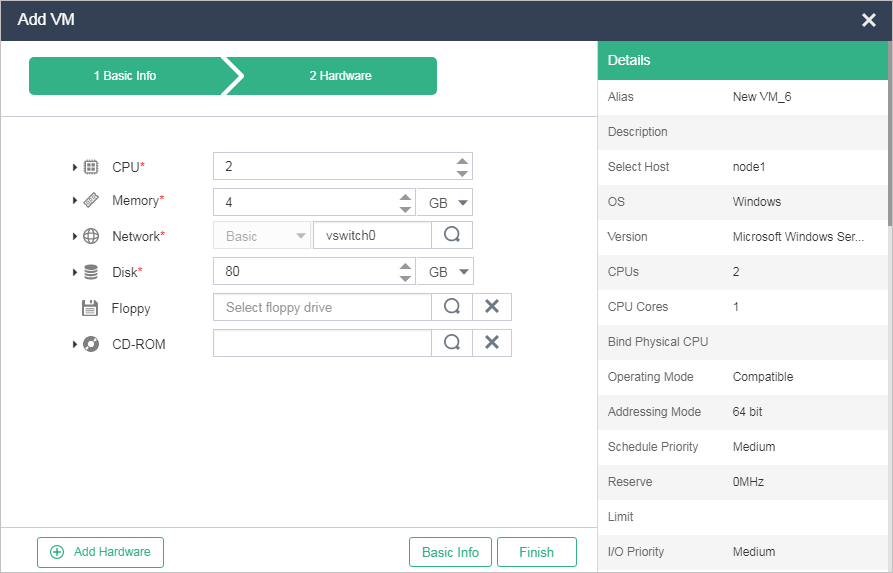
On the page that opens, click Add. After configuring basic settings, click Hardware to configure advanced settings or click Finish to complete VM creation.
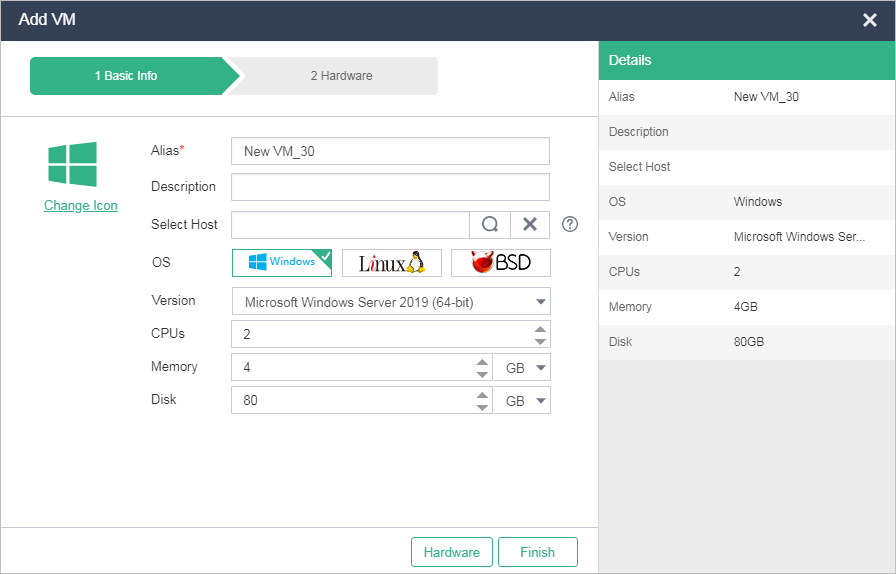
Figure-1 Configuring basic settings for the VM
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Alias |
Enter an alias for the VM. You can edit the alias after creating the VM. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the VM. You can specify different description to distinguish VMs with the same name. |
|
Select Host |
Select a host for VM deployment. If you do not select a host, the system automatically place the VM on a host selected based on the criteria of fewest VMs, lowest memory usage, and lowest CPU usage. |
|
OS and Version |
Specify the guest OS to install in the VM. The OS you actually install must be the same as the selected OS in type and version. |
|
CPUs |
Specify the number of vCPUs. The number of vCPUs of a VM cannot exceed the number of the CPUs on the host. |
|
Memory |
Specify the memory capacity of the VM. This setting is the memory size of the guest OS. The maximum memory size available for the VM depends on the physical memory size. |
|
Disk |
Specify the disk size. |
In the advanced settings, expand the CPU option to configure CPU parameters.
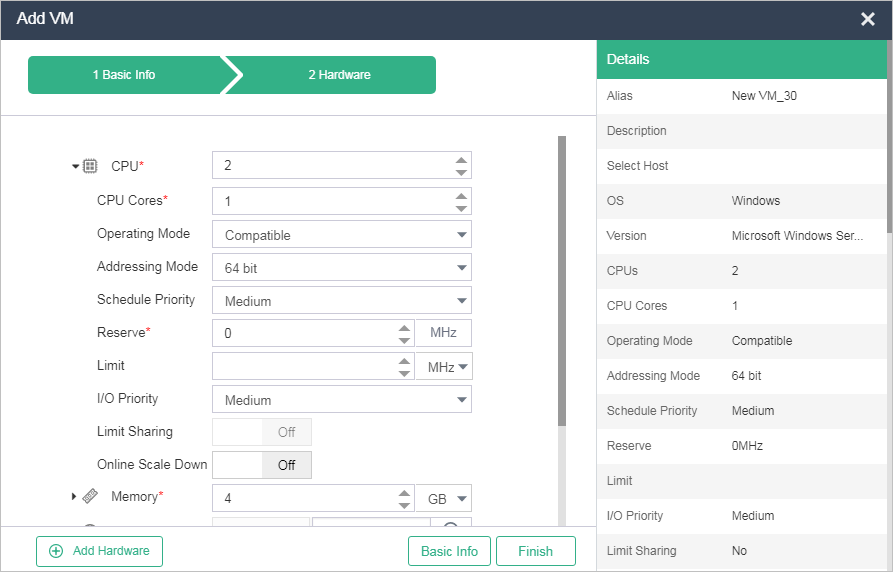
Figure-2 Configuring CPU parameters for the VM
Table-2 CPU parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
CPU |
Specify the number of vCPUs. The number of vCPUs of a VM cannot exceed the number of the CPUs on the host, but the total number of vCPUs of multiple VMs can exceed the number of CPUs on the host. In the system, a VM is a process in the kernel operating system. The kernel schedules processes based on time slices. When the time slice for a process is used up on a CPU, the process will be suspended, and the CPU is passed to the next process. Therefore, more CPUs assigned to a VM means more CPU time slices available to the VM processes and higher performance of the VM. |
|
CPU Cores |
Specify the number of CPU cores. The default value is 1. The number of CPU cores of a VM cannot exceed that of the host. |
|
Bind Physical CPU |
Bind the vCPUs of the VM to physical CPUs of the host. After that, the VM can use only the bound physical CPUs. This parameter helps reduce cache misses during process switchover among multiple CPUs. Although the binding can improve the VM operation efficiency, it affects CPU load balancing in the Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) from the perspective of process scheduling in the entire system. A vCPU cannot be bound to physical CPUs across NUMA nodes. To ensure successful VM operations (for example, migrate, clone, restore, and export operations) between two hosts, you must make sure the source and destination hosts use the same NUMA architecture. This option is only available after you select a host. |
|
Operating Mode |
Select a CPU operating mode. Options include Compatible (default mode) and Straight-Through.
|
|
Addressing Mode |
Select an addressing mode that matches the guest OS. Options include 64 bit (default) and 32 bit. You must select 64 bit mode if you are installing a 64-bit OS. If you select 32 bit mode for a VM that uses a 64-bit OS, the VM cannot start after being shut down. |
|
Schedule Priority |
Select a priority for the processes on the VM to obtain physical CPU resources during a contention. Options include High, Medium, and Low. When the physical CPU resources are insufficient, VMs with High, Medium, and Low priorities use CPU time slices in the proportion of 4:2:1. Higher priority assigned to a VM means more physical CPU time slices available to the VM processes and higher performance of the VM. |
|
Reserve |
Enter the guaranteed minimum CPU frequency for the VM. |
|
Limit |
Specify the maximum clock frequency of the VM, in MHz or GHz. If you leave this parameter empty, the vCPU clock frequency is not limited. The value range for this parameter is 10 MHz to the CPU frequency of the physical host. |
|
I/O Priority |
Select an I/O priority for the processes on the VM to read/write the disk. Options include Low, Medium, and High. When multiple VMs on a host perform disk read and write simultaneously, the VM with higher I/O priority has better performance. |
|
Limit Sharing |
Turn on or turn off limit sharing. For example, if you enable limit sharing for a VM that has 4 CPU cores and set the maximum host CPU frequency that a single CPU core of the VM can use to 2 GHz, the maximum host CPU frequency is 8 GHz for both the VM and a single CPU core of the VM. |
|
Online Scale Down |
Turn on or turn off online CPU scale-down, which allows online reduction of CPUs. T |
In the advanced settings, expand the Memory option to configure memory parameters.
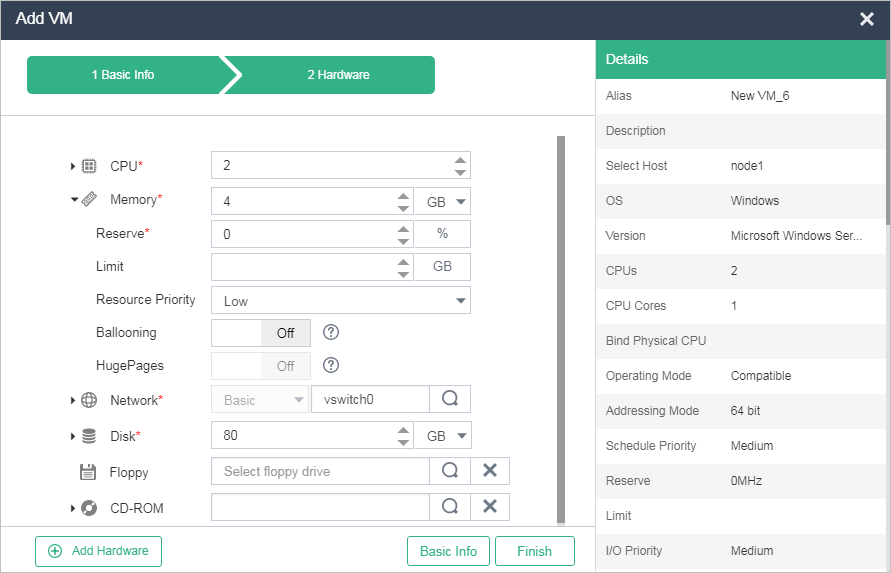
Figure-3 Configuring memory parameters for the VM
Table-3 Memory parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Memory Size |
Specify the maximum memory size of the VM's operating system, in MB or GB. The value range for this parameter is 512 MB to the maximum memory size of the host. In the system, memory resources are allocated to VMs on an on-demand basis. Therefore, the total size of memory that you specify for all VMs on a host can exceed the physical memory size of the host. However, memory overcommitment is not recommended in actual production environments because redundant memory resources are required if DRS, HA, DPM, affinity, or anti-affinity services are configured. Specify the memory capacity of the VM. This setting is the memory size of the guest OS. The maximum memory size available for the VM depends on the physical memory size. |
|
Reserve |
Specify the memory to be reserved for the VM to the maximum memory of the VM in percentage. 0 indicates that no memory is reserved. When the load of the VM increases and all the reserved memory has been used, the VM can retain the reserved memory even if it is idle. The host allocates memory to VMs based on the actual memory usage of the VMs. You can reserve some memory for a VM in case the VM needs more memory after the host memory is exhausted. |
|
Limit |
Enter the maximum host memory capacity that the VM can use. |
|
Resource Priority |
Specify the priority that the VM has when it requests memory. Options include Low (the default), Medium, and High. When the VM requests more memory than its reserved memory, the host makes its memory allocation decision based on the resource priority if memory contention occurs. |
|
Ballooning |
To dynamically distribute memory among VMs without shutting down the VMs when memory contention occurs, turn on this option. |
|
HugePages |
Enable or disable the VM to use HugePages memory of the host. You can turn on this option only if the HugePages feature is enabled on the host and the VM is shut down. In addition, this feature is mutually exclusive with memory reservation, memory limit, resource priority, and ballooning. |
In the advanced settings, expand the Network option to configure network parameters.
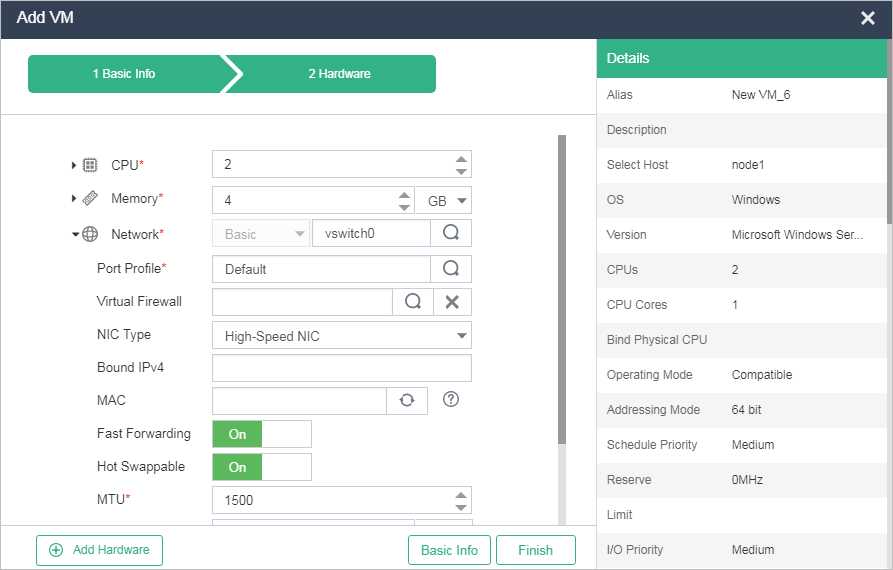
Figure-4 Configuring network parameters for the VM
Table-4 Network parameters
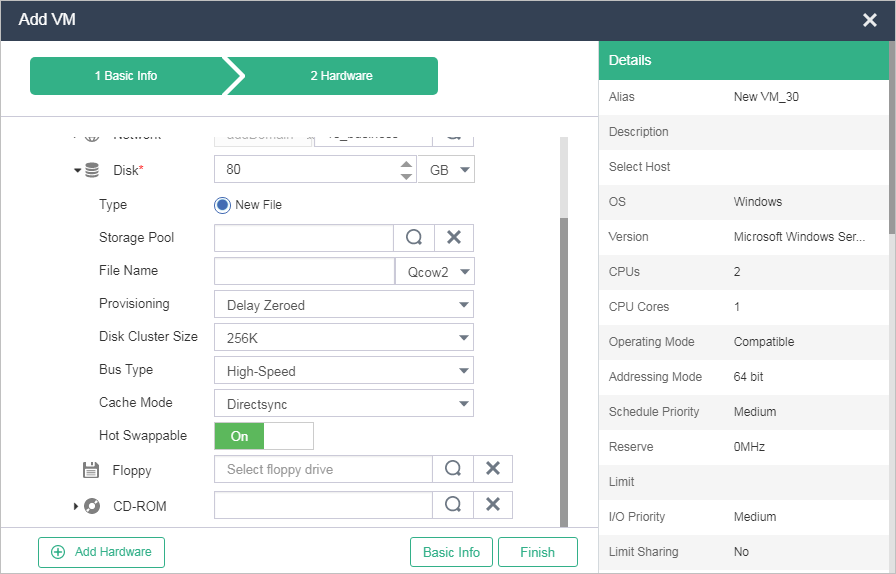
In the advanced settings, expand the Disk option to configure disk parameters.
Figure-5 Configuring disk parameters for the VM
Table-5 Disk parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Disk |
Specify the disk size. |
|
Type |
Specify the storage service type of the disk, which can be file or block storage. Options for file storage include New File or Existing File. By default, a new file is created as the disk for the VM. Disk type options are available only if a host is selected when you create the VM. If no host is selected, the value for this option can only be New File.
|
|
Storage Pool |
Select the storage pool on which the new disk is created. |
|
File Name |
Enter the file name of the disk if a new file is used as the disk. Select a disk formatting mode, which can be High Speed and Intelligent (the default).
|
|
Provisioning |
Select a volume provisioning mode. Options include Thin (the default), Lazy Zeroed, and Eager Zeroed.
|
|
Bus Type |
Select a bus type. Options include IDE, USB, High-Speed (the default), and High-Speed SCSI.
|
|
Cache Mode |
Select a data caching mode for the VM. Options include Directsync (the default), Writethrough, Writeback, and None. Different caching modes provide different read/write performance.
|
|
Hot Swappable |
Enable or disable disk hot swapping. This option is available only for the high-speed bus type. |
In the advanced settings, select a floppy drive, and then expand the CD-ROM option to configure CD-ROM drive parameters.
Figure-6 Configuring floppy and CD-ROM drive parameters for the VM
Table-6 Floppy and CD-ROM drive parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
Floppy |
Select a floppy drive image. The system will automatically load the high-speed driver compatible with the selected operating system version. |
|
CD-ROM |
Select a CD-ROM drive image. You can select an ISO image file for installing the operating system on the VM. |
|
Connection Mode |
Select a connection mode. Options include CD/DVD and Image File (the default). |
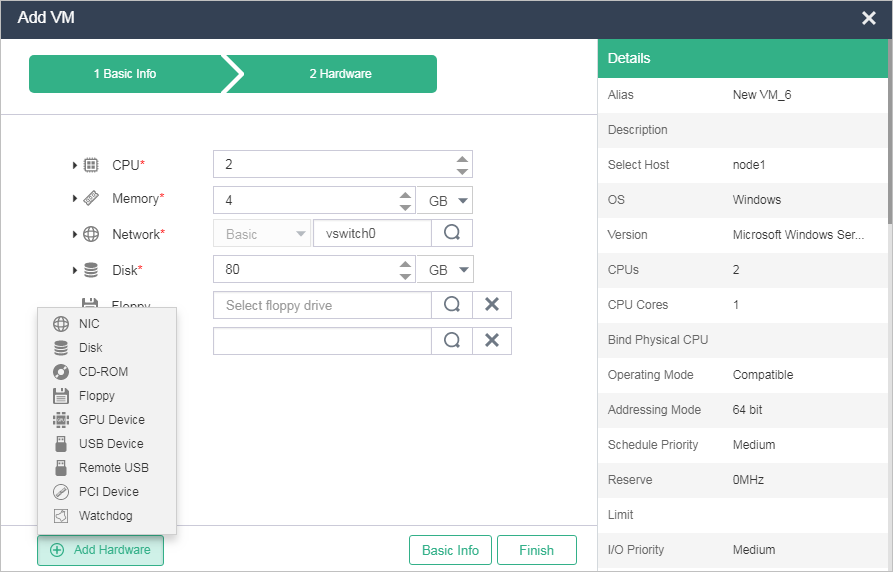
Click Add Hardware to select hardware options to add for the VM. Options include NIC, Disk, CD-ROM, Floppy Disk, GPU Device, USB Device, Remote USB Device, PCI Device, and Watchdog.
Figure-7 Adding hardware
Table-7 Hardware parameters
|
Hardware |
Parameter |
Description |
|
GPU Device |
Resource Pool |
Select a resource pool, which contains all available GPUs in the cluster. |
|
Service Template |
Select a service template. The service template defines the priorities for VMs to access the resources (such as GPU and HBA). The host allocates the resources to VMs based on the priorities of the VMs if the resources are insufficient. |
|
|
Driver Type |
Set the GPU driver type. Only the VFIO driver is supported. |
|
|
USB Device |
Connection Mode |
Set the USB connection standard. Options include USB 1.0, USB 2.0, and USB 3.0 (the default). This option is available only if you select a host when you create the VM. |
|
Remote USB |
Connection Mode |
Set the network USB connection standard. Options include USB 1.0, USB 2.0, and USB 3.0 (the default). This option is available only if you select a host when you create the VM. |
|
PCI Device |
Driver Type |
Set the PCI device driver type. Options include KVM and VFIO (the default). This option is available only if you select a host when you create the VM. |
|
Watchdog |
Add a watchdog to the VM. Interrupt options include Reboot (the default), Power Off, and Migrate. |
|